
Acute ruptures of extensor mechanism
359
Diagnosis
Extensor mechanism is interrupted when
patellar tendon is torn. The patient is unable to
actively extend the knee against gravity, or to
hold this position. The patellamoves proximally
as it is pulled by the quadriceps. A gap is easily
palpable where the patellar tendon is torn. Most
of the ruptures occur at the inferior pole of the
patella, but may also occur in the tendon mid-
body or, rarely, at the insertion on the tubercule.
The patella is proximally displaced as a result
of associated retinacular and capsular disruption
caused by the strong pull of the quadriceps
mechanism. It is also very mobile when moved
medio-laterally.
On standard radiographs, the patella is
proximally displaced (patella alta). Axial
patello-femoral view shows a “sunrise”, the
joint line disappears, because of overlapping
the patella and the femoral condyles on
radiographs. Many radiological indexes have
been described to evaluate the height of the
patella [22] and to compare it to the contralateral
side:theInsall-Salvatiindex[8],theBlackburne-
Peel index, and the Caton-Deschamps index.
We prefer using the Caton-Deschamps index as
it can be measured on any knee profile
radiograph with knee flexion between 10 and
80°, as compared to the Insall-Salvati index
which can be measured on 30° of knee flexion
radiographs. These indexes are useful for the
diagnosis and in post-operative follow-up.
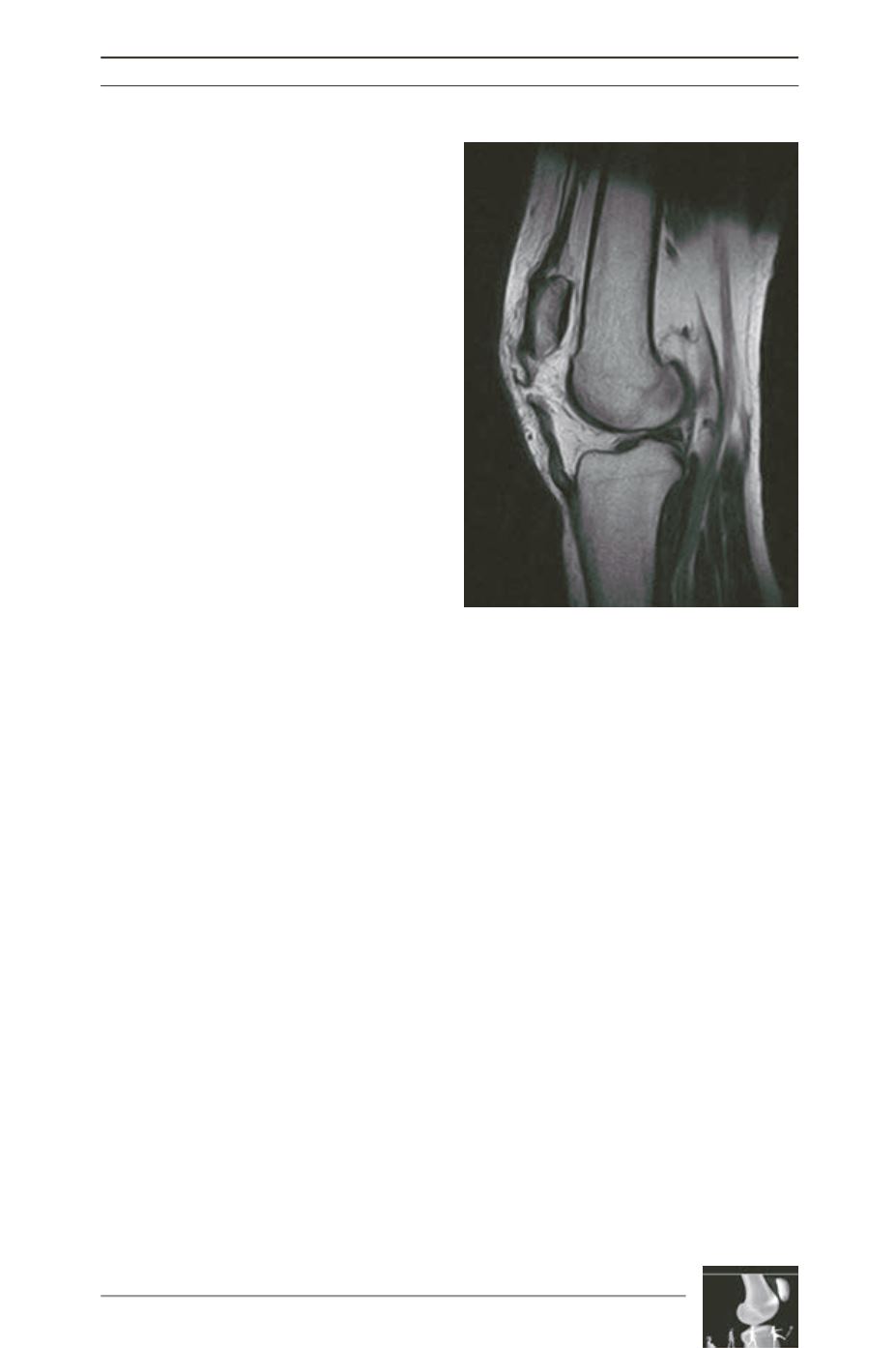
As for the quadriceps tendon, echography and
MRI are very useful to confirm and precise the
tear (fig. 2) [15]. MRI also allows to diagnose
associate lesions as anterior cruciate ligament
tear or meniscal tear that can occur during high
energy direct trauma.
Treatment
An acute repair of the patellar tendon during
the week following the trauma gives the best
results [15]. Many surgical techniques can be
used [5].
Historically, it was recommended that all
immediate repairs of the patellar tendon be
reinforced by external devices [23]. Several
reports have described reinforcing the repair
with various augmentation grafts, including
autografts, allografts (fascia lata, semitendino
sus, gracilis), and synthetic grafts (Mersilene,
Dacron, carbon fiber, and a poly-p-dioxannone
cord). However, clinical reports have demons
trated satisfactory results of acute patellar tendon
disruption repaired without augmentation [9].
We prefer reinforcing the repair with a
semitendinosous autograft and/or with an
augment with a PDS band, according to the
quality of the suture. We do not recommend a
metallic frame because it may sagitally tilt the
patella and it implies another surgery to remove
it. A straight incision is made on the medial
border of the patellar tendon. The patellar
tendon paratenon is incised longitudinally and
preserved for repair at the time of closure.
Fig. 2











