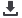
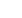
Patient specific instruments in total knee replacement
15
Discussion
We found in our series encouraging results
similar to those reported in CAS.
However PSI, because of manual segmentation
of the MRI, can show variation in the clinical
results and in post op frontal alignment because
of non appropriate fitting of the guides when
placing on the femoral or tibial bone [2].
In several series, the use of PSI did not reduce
blood loss, but in these series the tourniquet
was used and we have no information about
how the hemostasis was conducted [3].
Conclusion
In our series, the PSI were reliable and
reproducible. However, this technique still
requires a manual step for MRI segmentation
and to define anatomical points. These
drawbacks could introduce a bias in the
accuracy of the segmentation, and so, in the
guides manufacturing.
Nevertheless, the results of this new technique
are encouraging. The PSI technique still
remains submit to variability, and won’t be
improved until all the procedure is
computerized.
Literature
[1] D Saragaglia, F Picard, C Chaussard, E
Montbarbon, F Leitner, P Cinquin. Mise en place
des prothèses totales du genou assistée par ordinateur :
comparaison avec la technique conventionnelle.
Rev Chir
Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2001 Feb 1;87(1): 18-28.
[2] Russell R, Brown T, Huo M, Jones R. Patient-
Specific Instrumentation Does Not Improve Alignment in
Total Knee Arthroplasty.
J Knee Surg. 2014, Feb 6.
[3] Thienpont E, Grosu I, Paternostre F,
Schwab PE, Yombi JC. The use of patient-specific
instruments does not reduce blood loss during minimally
invasive total knee arthroplasty?
Knee Surg Sports Traumatol
Arthrosc. 2014 Mar 27.