EXTENSION DEFICIT AFTER ACL RECONSTRUCTION…
211
because mobilization to regain extension can
lead to graft rupture. After deflating the
tourniquet, meticulous haemostasis was
performed. One suction drain was inserted in
the posterolateral portal and left in place for
24 hours in order to avoid post-operative
haematoma. The arthrotomy was left open. The
iliotibial band, the medial retinaculum, the
subcutaneous tissues and the skin were sutured
at the end of the procedure.
Postoperative rehabilitation
Patients were placed in an extension brace for
the first post-operative night only. A continuous
passive motion (CPM) machine was not used.
Intensive physiotherapy with several sessions a
day began on the first post-operative day with
special emphasis on quadriceps awakening. It
included manual mobilization, full passive and
active-assisted ROM exercises and patellar
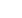
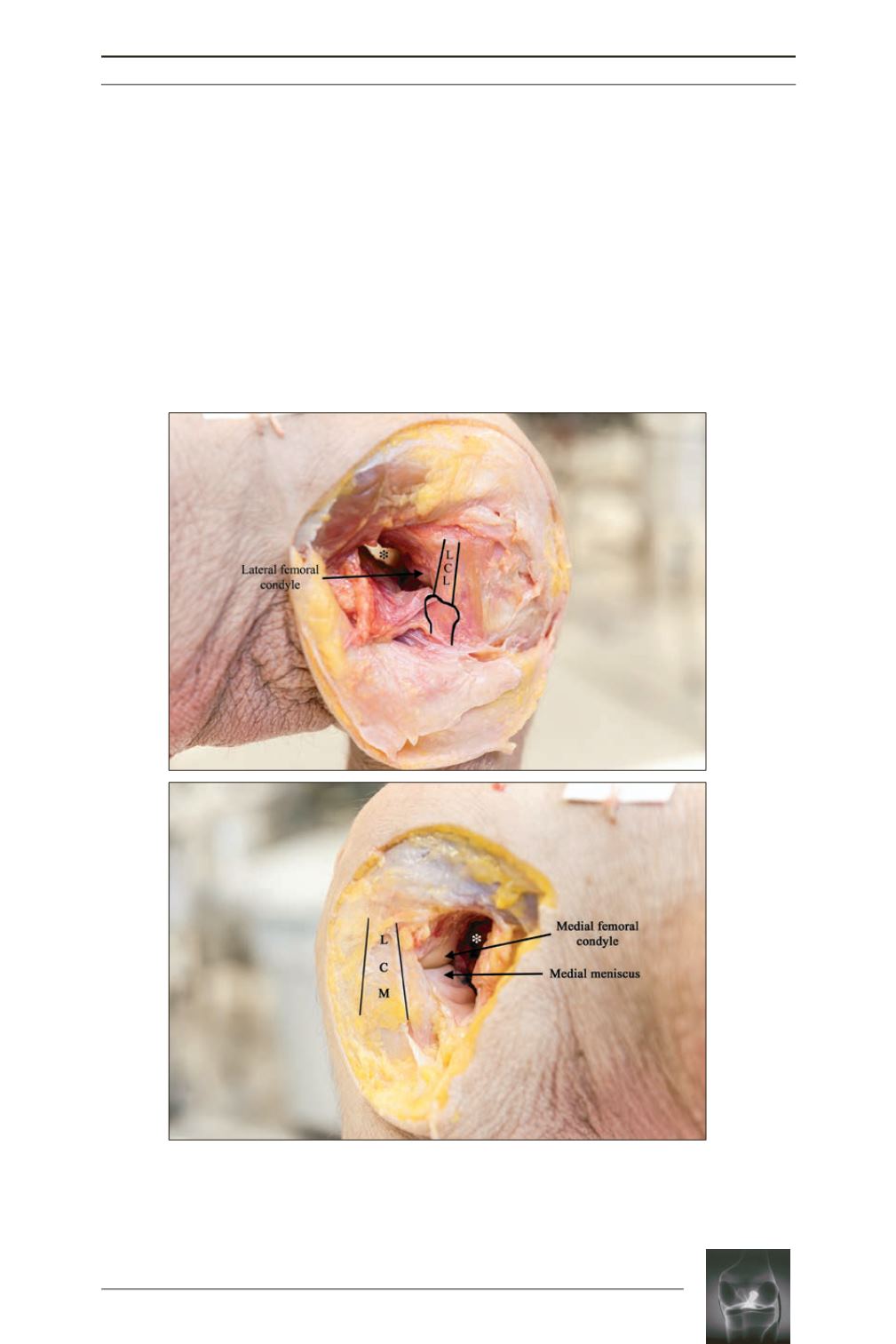
Fig. 1:
Cadaveric dissection of a right knee:
a:
Lateral view: retroligamentous approach showing the posterior space behind
the femoral condyles (
LCL:
lateral collateral ligament; * posterolateral recess).
b:
Medial view: “femoral peeling” by the posteromedial retroligamentous approach
(MCL: medial collateral ligament; * posteromedial recess).
a
b