ANTEVERSION AND LENGTH OF THE FEMORAL TUNNEL IN ACL RECONSTRUCTION…
91
antero-medial portal, we compared two
femoral tunnel-drilling techniques: the first
technique used rigid instrumentation with the
knee flexed at 120° (Rigid Population) and the
second used flexible instrumentation with the
knee flexed at 90° (Flexible Population).
Excluded from the study were: revision of
ligament reconstructions, ligament reconstruc
tions with an extra-articular lateral tenodesis,
ligament reconstructions of hamstring tendons
and double-bundle ligament reconstructions.
Surgical technique and instruments
Patients were positioned with their leg hanging
down and their thigh placed on a leg holder. An
arthroscopic investigation confirmed the
ligament rupture.
The femoral tunnel was drilled via the antero-
medial portal using rigid or flexible
instrumentation, as determined by rando
misation. The two Rigid and Flexible
instruments were from the same Versi-Tomic®
system (Stryker®) (fig. 1, 2).
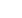
Regarding the Rigid instrumentation, the knee
was flexed at 120°; the rigid guide pin was
inserted into the femur using an aimer offset by
6mm hooked behind the lateral condyle. The
femoral tunnel was then drilled 10mm using a
rigid reamer following the axis of the guide pin.
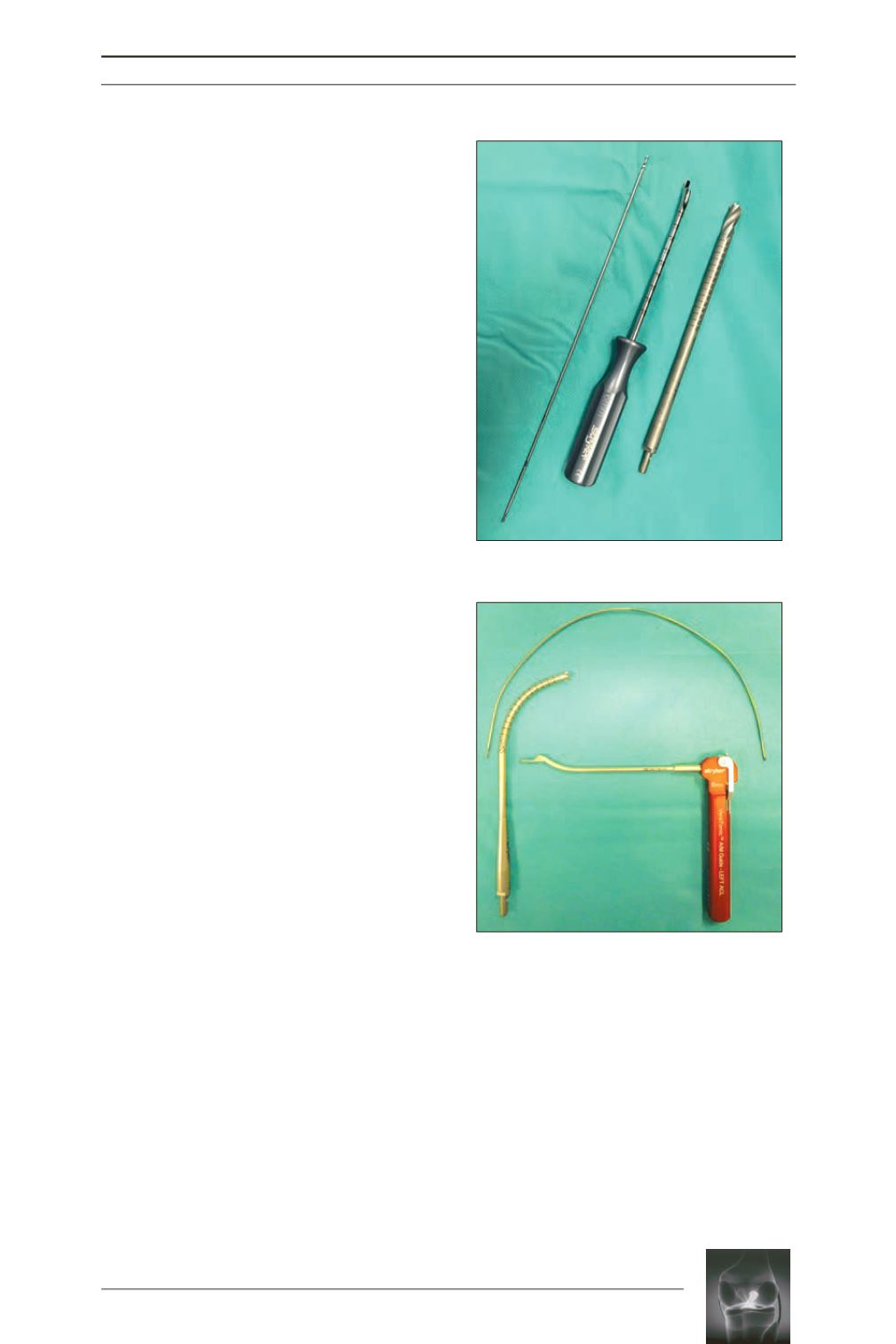
Regarding the flexible instrumentation, the
knee was flexed at 90°; an aimer hooked behind
the lateral condyle and offset by 6mm was
used; however, its articular extremity was
anteverted at 42° thereby providing the flexible
pin with a 42° forwards angularity; during the
drilling, the 10mm flexible reamer then
followed the direction imposed by the pin.The
tunnels were blind-ended in both cases, and an
endobutton systematically used for fixation.
Evaluation method
The height of the patient was measured during
the pre-surgical consultation.
The length of the femoral tunnel was measured
during the procedure by directly reading the
gauge intended for this purpose (fig. 3). The
positioning of the femoral tunnel was measured
on the post-surgical radiography profile, by an
independent operator (radiologist) (fig. 4).
Fig. 2:
Flexible instruments
Fig. 1:
Rigid instruments