G. LA BARBERA, M. VALOROSO, G. DEMEY, D. DEJOUR
102
Knee arthroscopy is performed through two
anterior portals: the antero-lateral (AL) portal
is done close to the patellar tendon and the
antero-medial (AM) one is performed at the
same level and 15mm medially to the patellar
tendon. After standard knee examination,
meniscal and cartilage lesions are addressed if
required. The anterior fat pad is debrided to
allow adequate notch visualization, paying
attention to preserve the native ACL tibial and
femoral insertions, as they serve as anatomic
landmarks for tunnel positioning [6] (fig. 1).
The center of the ACL femoral insertion site
can be located using the residual ACL footprint
and the lateral intercondylar and bifurcate
ridges [7] (fig. 2). With the knee at 90° of
flexion, a 5mm offset outside-in femoral guide
(SBM SA, Lourdes, France) is introduced
through the AM portal and placed at ACL
femoral insertion site. The external part of the
femoral guide is located on the lateral com
partment of the knee. A lateral longitudinal
skin incision of 2cm is performed at the point
indicated by the femoral guide. The incision is
straight to the bone through and parallel to the
iliotibial band fibers. The inferior limit of the
incision is represented by the proximal
insertion of the lateral collateral ligament and
postero-lateral complex. The OI femoral guide
is positioned at 45° in the axial plane and 30° in
the frontal plane. Finally the pin is drilled [8]
(fig. 3).
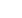
Fig. 1:
ACL bundles evalu
ation. The preservation of
the native ACL tibial and
femoral insertions is useful
because they serve as
anatomic landmarks for
tunnel positioning.
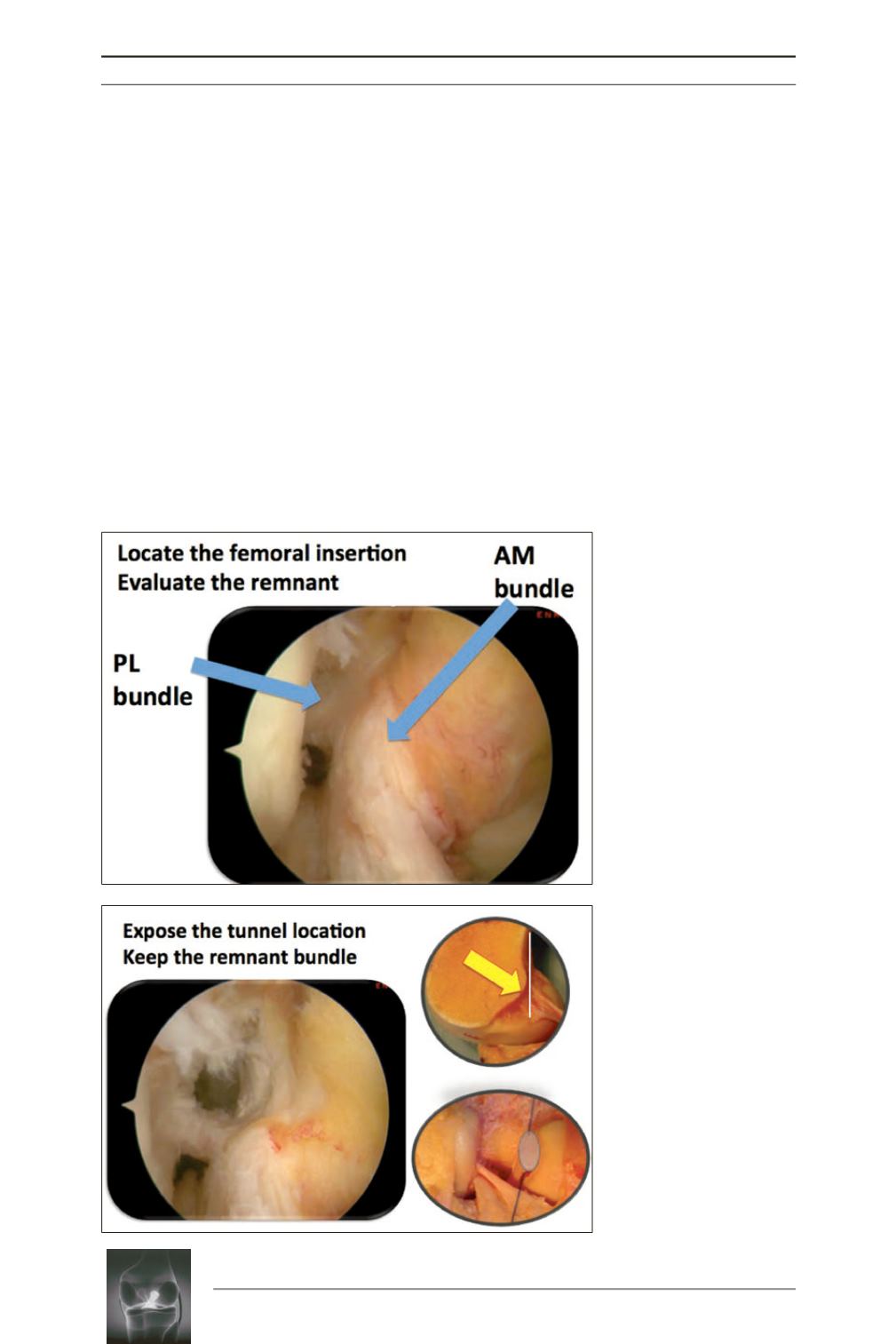
Fig. 2:
The center of the ACL
femoral insertion site can be
located using the residual
ACL stump. Femoral tunnel
location is exposed keeping
intact the remnant bundle.
Femoral footprint is half a
circle behind the posterior
cortical line.