WHAT ARE THE INTRINSIC FACTORS IN ACL FAILURE?
173
slope correction should be taken into
consideration and performed when values
superior to 12º are measured [8]. PTS
inclination is influenced also by the presence of
the menisci that shift the tibial slope towards
the horizontal as described by Lustig
& al.
[9].
In this context, meniscal lesions or a previous
meniscectomy may theoretically increase PTS.
The treatment of the meniscal tears (repair or
replacement) seems to be recommended not
only to reduce the incidence of osteoarthritis,
but also to protect the ACL graft.
ANTERIOR TIBIAL
TRANSLATION AND
ROTATORY LAXITY
The anterior knee laxity is an important factor in
predicting ACL status both in ACL-ruptured and
ACL-intact patients [4]. Several devices are
available to quantify the knee laxity in pre-
operative and post-operative ACL reconstruction
assessment. However, a lot of them are examiner
dependent and a potential overestimation of the
laxitycanoccur.Therefore,acarefulinterpretation
of their results is required. The most popular tools
to measure the knee laxity are: KT-1000
TM
and
KT- 2000
TM
Knee Ligament Arthrometer (KT-
1000
TM
, KT-2000
TM
; MEDmetric Corp, San
Diego, California), the Rolimeter
TM
(Aircast
Europa, Neubeuern, Germany), and the stress
radiography Telos
TM
device (Telos GmbH,
Laubscher, Holstein, Switzerland). Uhorchak
& al.
[10], in a prospective study, observe that the
relative risk for sustaining an ACL rupture is
increased by 2,7 times in female subjects who
have increased knee laxity measured by KT-
2000
TM
[4]. In a prospective study comparing
Telos
TM
to Rolimeter
TM
in patients with ACL
lesion, Panisset
& al.
[11] observe that the
association of the side to side difference (SSD)
>5mm with Telos
TM
and positive pivot-shift test
has a sensitivity of 88%and a specificity of 94,6%
(P<0.01) for complete ACL rupture. Instead the
combination of SSD >5 mm with Rolimeter
TM
and positive pivot-shift test has a sensitivity of
72,7% and a specificity of 92,4% (P<0.01) in case
of complete ACL tears [11] (fig. 3).
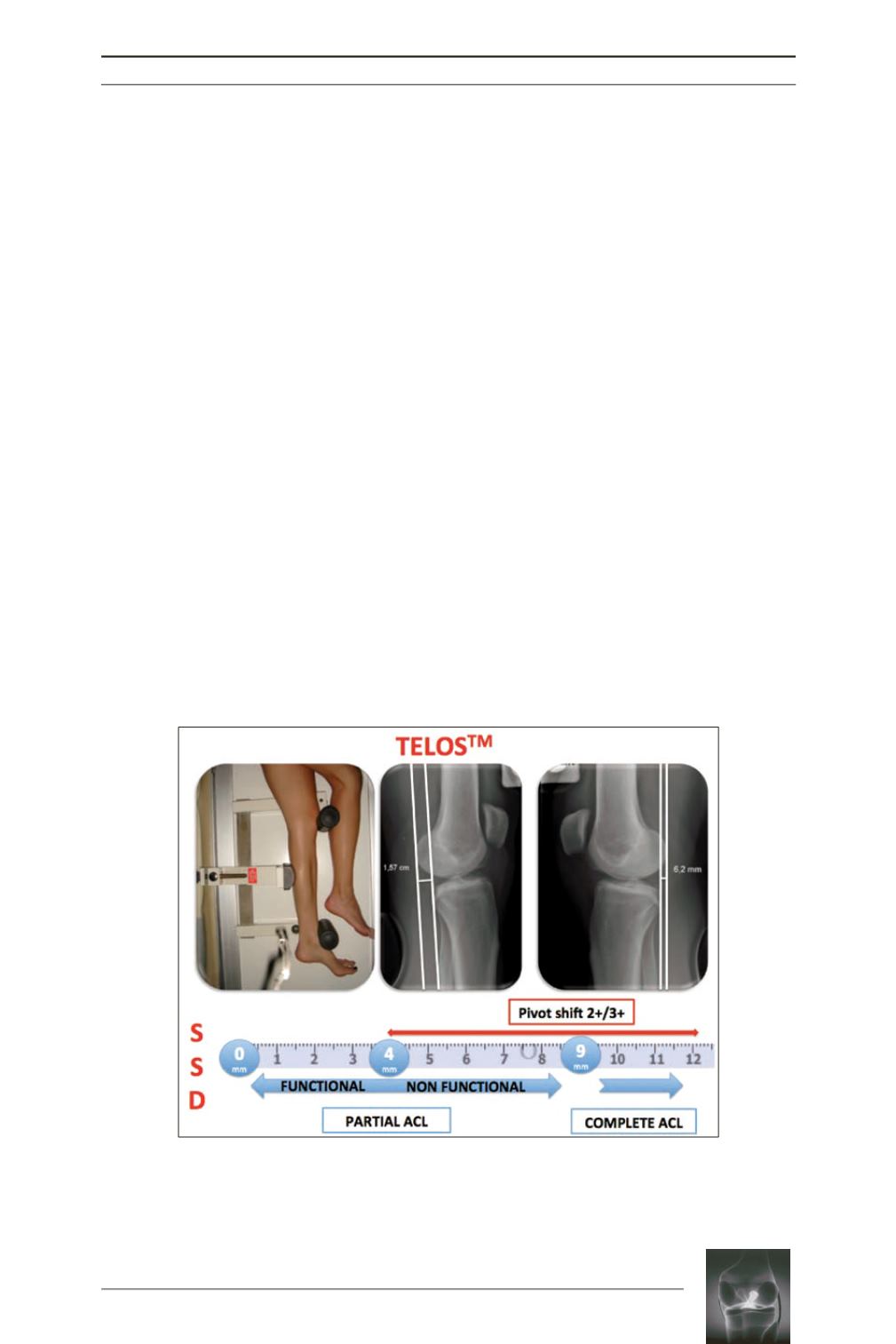
Fig. 3:
Correlation between SSD with TelosTM, pivot-shift test and arthroscopic
ACL injury pattern:
< 4 mm: partial tear - functional remnant - pivot shift test 0/1+
4-9 mm: partial tear - non functional remnant - pivot shift test 2+/3+
> 9 mm: complete tear - pivot shift test 2+/3+