O. RACHET, B. QUELARD
202
Those four goals are the four key points of
rehabilitation.
KEY POINT N° 1:
WAKENING
THE QUADRICEPS
Wakening the quadriceps, which inhibition is
extremely frequent whatever the type of
transplant, will allow to recover the active
locking of the knee. This muscular awakening
is based on learning.
• Rapid voluntary contractions, called “flash”
of vastus medialis and vastus lateralis
(1 contraction/sec for 10 seconds then rest for
10 seconds), knee extended, patient in sitting
position to put the rectus femoris in impaired
functions.
• Static contractions maintained with maximal
and below pain intensity during the whole
duration of the contraction (contraction
lasting 10 sec then resting for 10 sec).
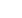
Contractions are done in the right way if the
vastus medialis can be seen, the patella pulls up
and the patellar tendon is stretched. Alleviating
the heel on the floor (fig. 1a, 1b) shows the
efficiency of the contractions.
KEY POINT N° 2:
RECOVERING
THE COMPLETE PASSIVE EXTENSION
During the days following surgery, to live the
knee in full extension is painful leading to a
reflex defense of the hamstrings and an antalgic
flexum can appear, and if he stay a long time,
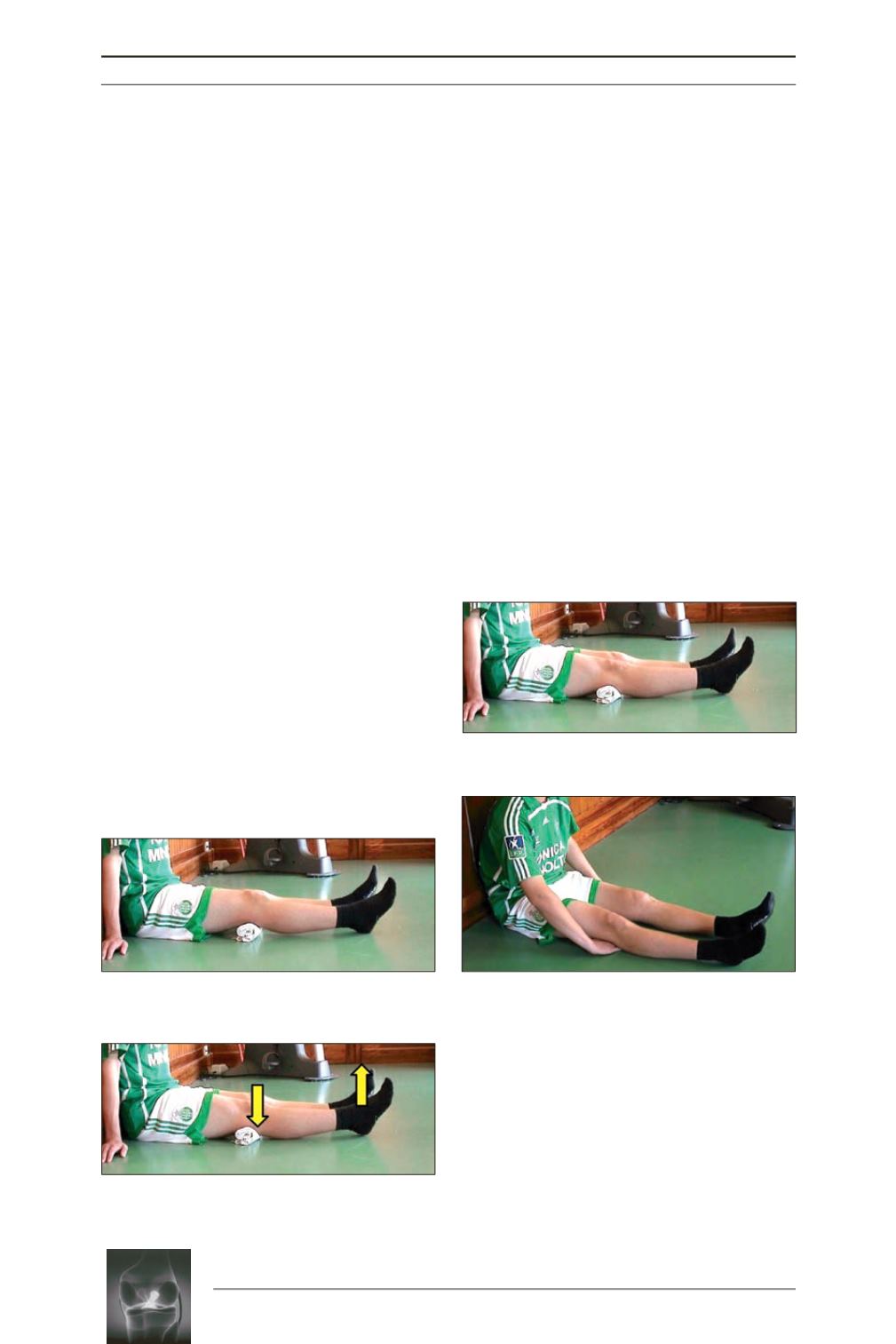
may be responsible for the foun’dation of a
cyclope. Loosening the posterior muscular
chain affects then the recovery of the 0° passive
extension. This loosening is gotten by putting a
rolled towel under the popliteal fossa (fig. 2a)
which towel is slowly smaller and smaller.
Combined with passive knee mobilizations
towards extension, soft and below pain, with
“flash” contractions of the vastus medialis and
lateralis, this towel will allow lto slowly
recover the full extension and is taken away as
soon as possible (fig. 2b).
KEY POINT N° 3:
RESTORING A
NORMALWALKING PATTERN
From the day of surgery, walking exercises
should be performed with relieved and
progressive weight bearing with the help
2 crutches in parallel position. The full weight-
bearing in static is recovered step by step by
Fig. 1a:
Resting position.
Fig. 2a
Fig. 1b:
Contraction of the quadriceps: marking the
poplieal fossa go down and at the same time the
pression of the heel on the floor decrease.
Fig. 2b