205
Anterior Cruciate Ligament reconstruction is a
safe surgical procedure and postoperative
complications are very rare.
Infection and deep veinous thrombosis are well
known and won’t be detailed here.
Despite the fact that early outcomes after ACL
reconstruction are very good and are not
influenced by the type of graft [2], delayed
complications can occur during a rehabilitation
period and when returning to sporting
activities.
Specific complications are related to the
harvesting site, tunnels and fixation material.
Delayed general complications may concern
anterior persistant knee pain, muscle weakness,
knee stiffness, secondary cartilage damage and
meniscal tears, and of course graft rupture.
SPECIFIC COMPLICATIONS
ON HARVESTING SITE
Away to avoid donor site morbidity is to use an
allograft. However the majority of surgeons
use tendinous autograft from hamstrings or
bone-tendon-bone graft from the patellar
tendon, each harvesting technique having its
own specific risks.
Harvesting btb graft can weaken the patella and
lead to a fracture during early rehabilitation
period [8]. Tibial tubercule fracture [1] and
patellar tendon avulsion are very rare and
authors described patello femoral instability due
to iatrogenic sagittal patella fracture [22].
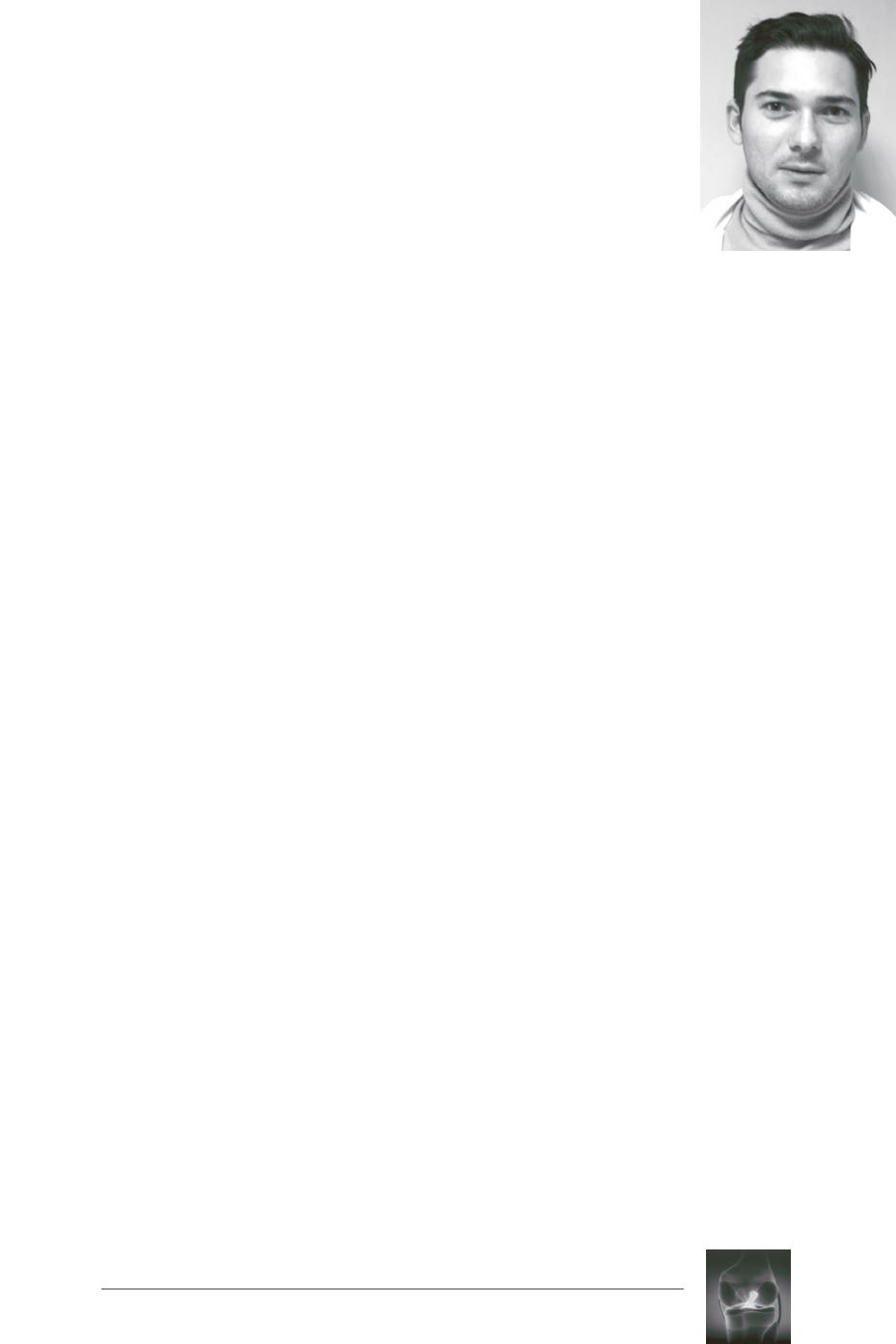
Patellar tendonitis is common and healing is
the rule with an adapted rehabilitation program,
chronical evolution with patellar tendon
ossification is very exceptional [7] (fig. 1).
RETURN TO SPORT
AND PREVENTION:
COMPLICATIONS - LITERATURE
A. PINAROLI, L. BUISSON, G. ESTOUR