
P.J. Erasmus, M. Thaunat
164
tight in extension end lax in flexion. It is further
recommended that the ligament should be
tightened in full extension, pulling proximally
on the patella with a bone hook in the direction
of the anterior superior iliac spine in order to
ensure that, with maximum quads contraction,
there will be more tension in the patellar tendon
than in the reconstructed MPFL (fig. 2). In
cases of severe patella alta a distal tibial
tubercle transfer should be considered as this
will decrease the non isometry of the
reconstruction allowing easier and more precise
tensioning of the reconstructed ligament [9]
(fig. 3). We will consider a distal tubercle
transfer where the Bernageau measurement is
more than 8mm or the patella tendon length
more is than 60mm, especially if this combined
with a clinically marked positive J-Sign. A
distal transfer of as little as 6mm is usually
adequate in these cases. Other authors have
recommended different techniques for
tensioning the reconstructed MPFL. The most
popular being to tension the ligament between
30° to 60° of flexion when the patella is already
centred in the trochlea [5, 20, 6]. The major
length changes in the MPFL happens after 30°
of flexion [25, 29] and considering this
tensioning the ligament in early flexion should
prevent over tensioning provided that, on the
femur, the correct non isometric point have
been selected.
Post operative quadriceps inhibition, although
temporary, can result in an increased rehabili
tation period and a late return to sporting
activities.
Drez [7] reported quadriceps atrophy in more
than 50% of his patients at an average follow
up of 31.5 months (24-43).
In an effort to combat this we start the patients
on isometric quads contraction program
preoperatively. Post operatively no braces are
used and immediate active and passive full
range of motion is encouraged.
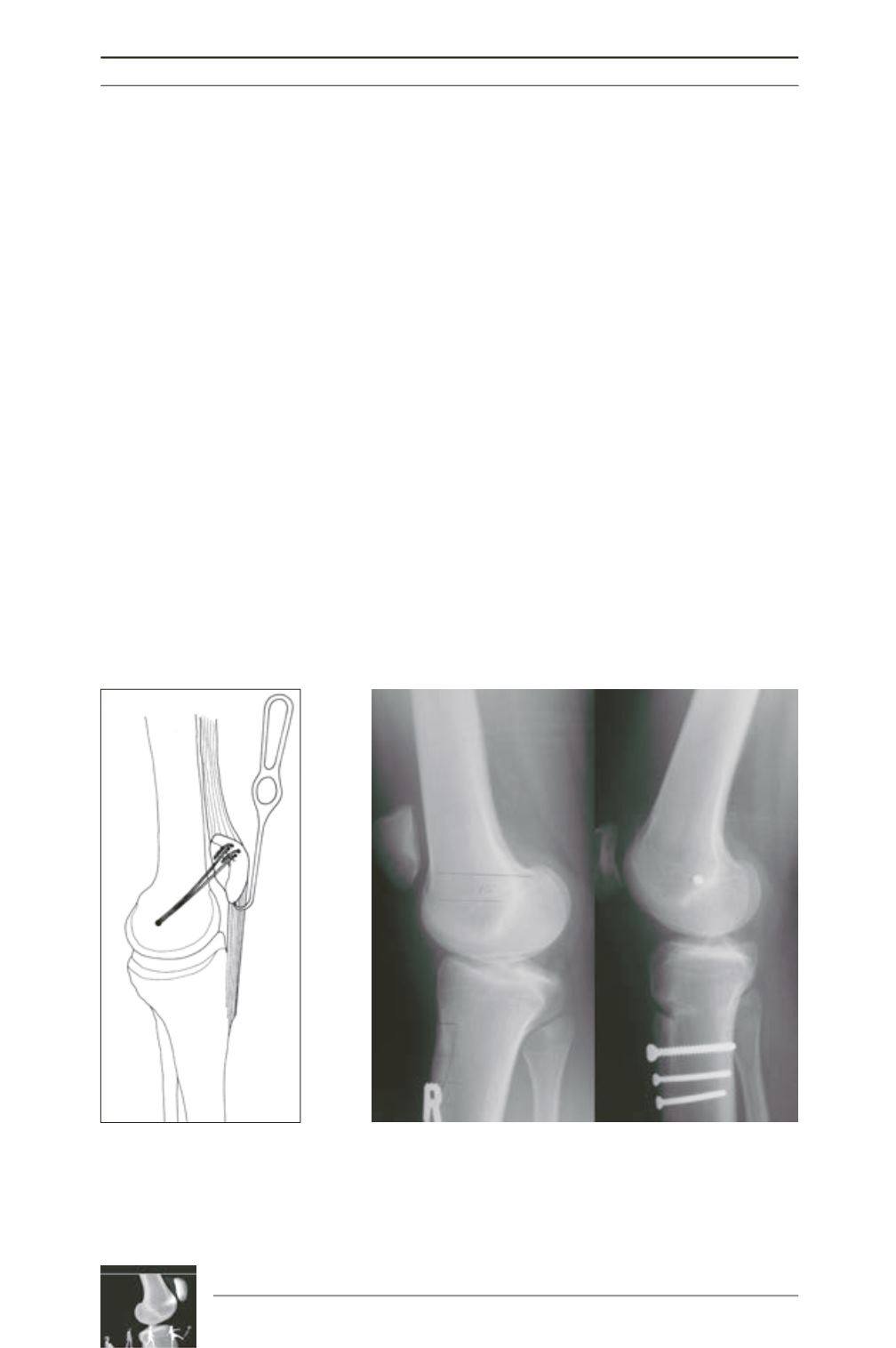
Fig. 2 : Tensioning the MPFL
graft in full extension ensuring
that the tension in the recons
truction is less than in the
patellar tendon.
Fig. 3 : Distalization of the tibial tubercle combined with a MPFL
reconstruction.











