R. Badet, S. Piedade
120
Tibial fixation
Fixed bearing
2 types should be distinguished:
Full polyethylene-piece
has the advantage of
avoiding the interfaces. An non progressive
radiolucent line on the tibia is common, but
clinical results are very satisfactory.
Tibial metal back
imposes the need of 9mm
polyethylene height. The fixation is done by
cement or by screws (which could be a cause of
loosening secondary to granulomas along the
screws).
Certain authors have criticized these systems
because they could create a peak of stress,
which could explaining some residual pain in
postoperative outcomes of UKA.
Mobile bearing
In 1974, Goodfellow has developed the concept
of mobile bearing aiming at reducing the stress
and wearing of the polyethylene. In this context,
the polyethylene implant is necessarily concave
with two congruent jaws (lips). This type of
implant is not suitable to lateral femorotibial
compartment because its hypermobility could
lead to a higher failure rates secondary of
polyethylene dislocation (10%).
Size and shape of tibial insert
Minimal access approach associated to
particularities of local anatomy has justified the
development of instruments well-matched for
proper evaluation of the depth and wide of
tibia. An Unsuitable implants could explain
some pain produced by the conflict between
implant and soft tissues.
Technical factors: surgical technique
Patient positioning and surgical approach
(evaluation of ligament and articular cartilage
status).
The patient is positioned supine, knee flexed at
90°. To mobilize the knee in all range of motion.
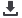
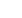
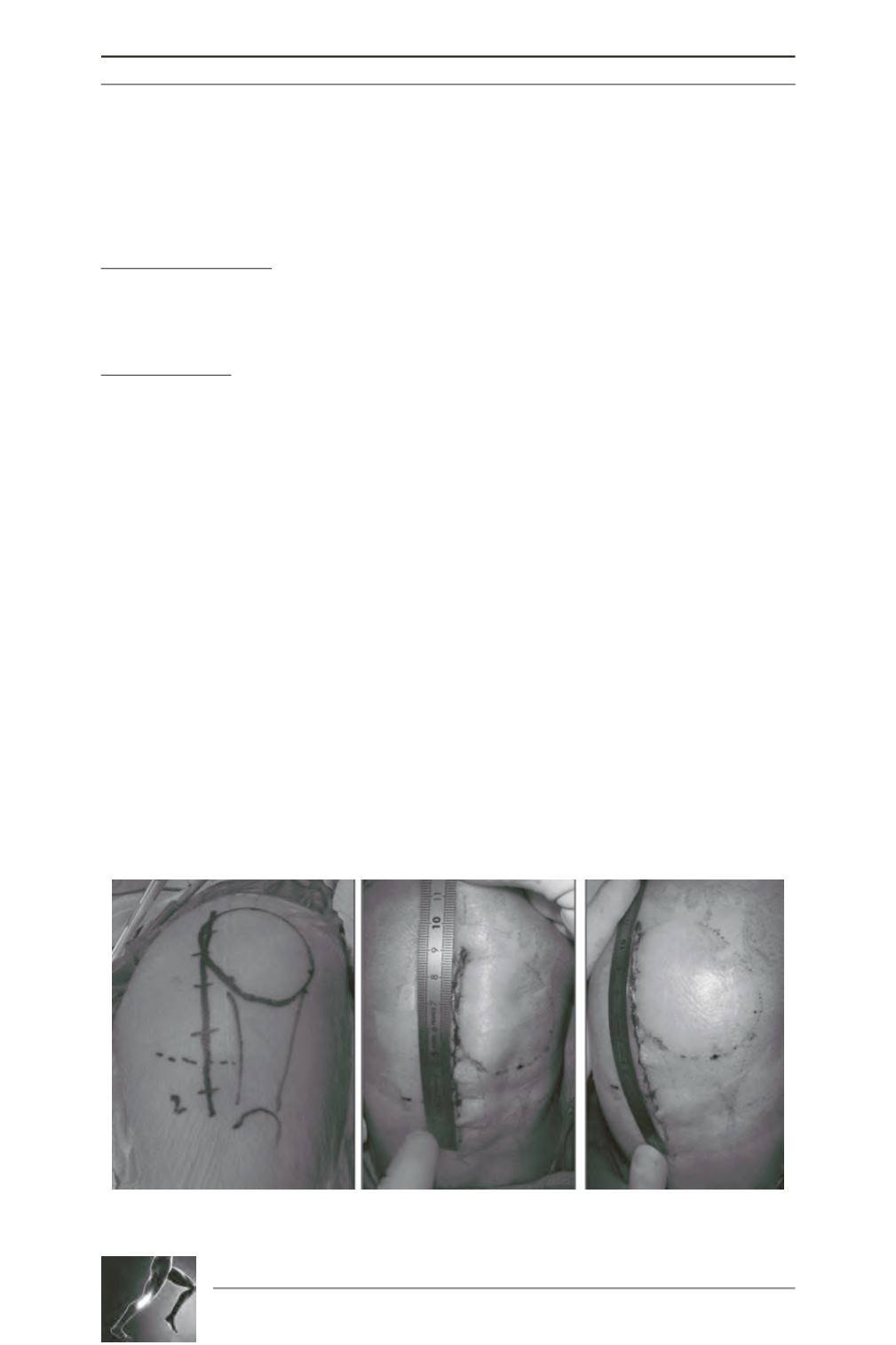
A lateral parapatellar approach is performed
extending from the superior pole of the patella
to 2 to 3cm below the joint line (fig. 1A to 1C).
The objective is to minimize invasive
procedures and consequently, promote
accelerated postoperative functional recovery.
In addition, whenever it is possible, the incision
across the quadriceps tendon as well the patellar
eversion should be avoided (fig. 1D).
Careful evaluation of articular cartilage on the
patellofemoral and femorotibial compartments
and ACL status must be done.
Fig. 1A at 1C: R Knee - Skin incision para patellar lateral approach: top of the patella to 2-3cms below
the joint line. 9cm extended knee 11cm flexion knee.
A
B
C