C. LUTZ, B. SONNERY-COTTET, M. DAGGETT, P. IMBERT
24
Quantitative anatomy
Length
The length of the ALL varies from 34,1mm
(12) to 59mm (4), with more similar values in
other studies: 37,3mm (5), 38,5mm (2),
39,1mm (7) and 40,3mm (1). The variations in
length between these different authors can be
explained by the problems identifying the
femoral insertion of this ligament and by the
knee position, in flexion and rotation, which
varied from one study to another.
Kennedy [6], when measuring lengths each 15°
between 0 and 90° of flexion, found an increase
from 36,8mm to 41,6mm.
In a previous study [7], we observed a
significant increase in the ALL length during
internal rotation at 30° flexion, with a mean of
10 mm, finding similar results to those reported
by Dodds [4] (mean lengthening, 9.9mm).
These variations in length during flexion and
rotation are important to consider for under
standing of ALL function and reconstruction.
Width
The width of the ALL increases from proximal
to distal with a mean at the femoral attachment
of 4,8mm and at the tibial attachment of
11,7mm for Caterine [1], and respectively 8,3
and 11,2mm for Claes [2]. Its structure is
narrow and tubular at the femoral origin and
wider on the tibia.
Thickness
ALL thickness varies from 1,3 to 2,7mm [1, 2,
5, 12].
Width and thickness indicate that the ALL is a
flat and broad structure.
Connections
ITB
For Dodds [4] and Claes [2], the ALL is
separate from the posterior fibers of the ITB,
specifically from the capsule-osseus layer.
Caterine [1] described superficial fibers
originating from the fascia of the lateral
gastrocnemius tendon insertion, proximal to
the lateral femoral condyle, overlying the
proximal portion of the ALL with a unique
attachment to the posterior portion of Gerdy’s
tubercle. These superficial fibers running in the
same orientation as the ALL can be confused
with the capsule-osseus layer of the ITB band
and explain why authors consider ALL as a part
of ITB [11, 12].
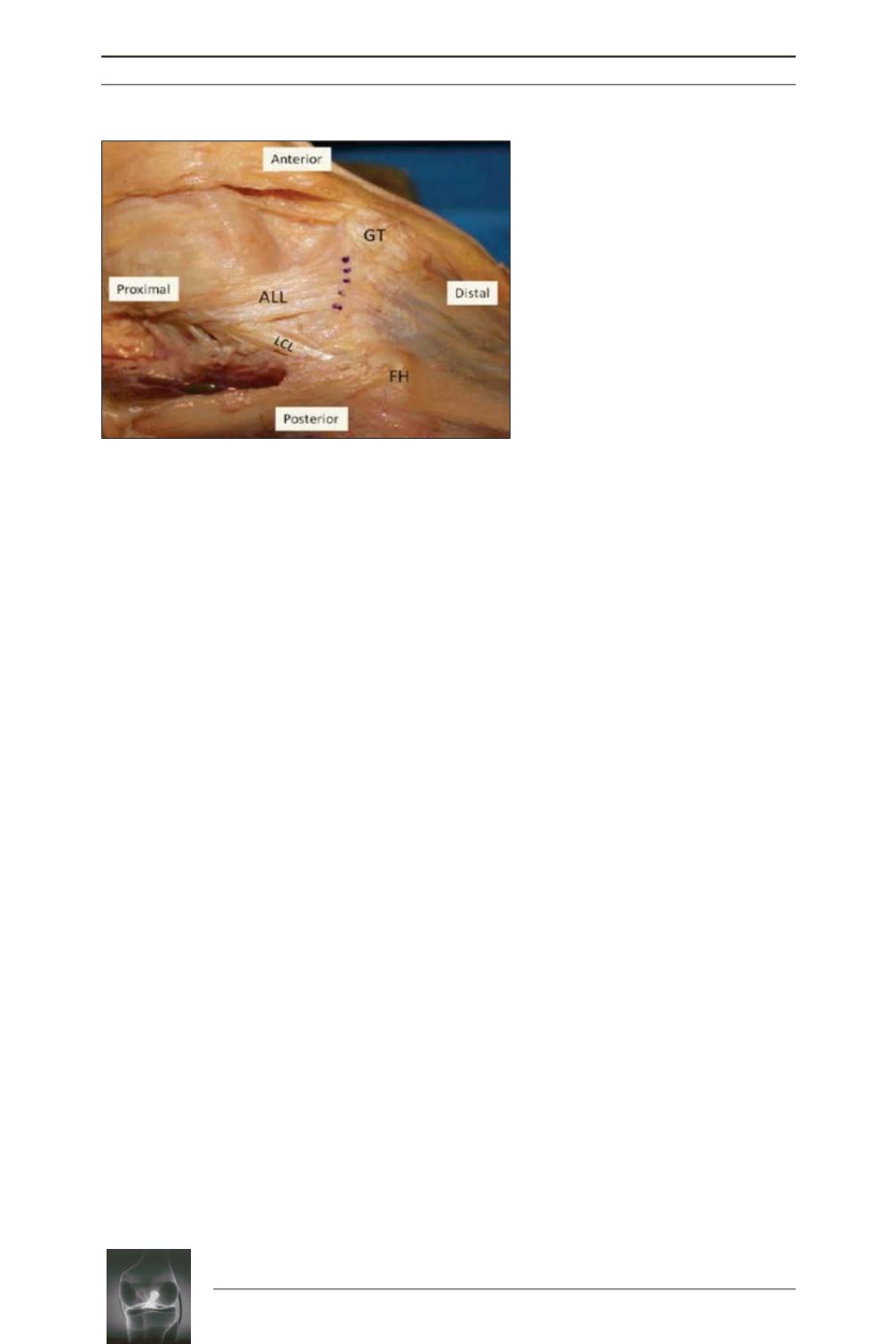
Fig. 5:
ALL tibial origin (dotted line) (
GT
=
Gerdy tubercle, A
LL
= anterolateral
ligament,
LCL
= lateral collateral
ligament, FH = fibular head).