GRAFT FIXATION
77
Currently, available fixation options include
interference screws (metal and bioabsorbable),
staples, suture and post, cross pins, expansion
bolts, suspension devices (cortical, cancellous
or cortical cancellous), or even an implant-free
press-fit fixation technique. All these fixation
devices have an ultimate load failure that
exceeds the 450 N safe early physiological
loading threshold proposed by Noyes and
coworkers (Table 2).
FEMORAL FIXATION
For Bone Patellar Tendon Bone (BPTB) graft,
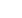
most surgeons prefer to use interference screws
because it results in the creation of a stiffer
construct. Interference screws were initially in
Fig. 2:
From Kurosaka
and coworkers
[4]
Fixation
Ultimate Load to Failure (N) Stiffness (N/m)
Patellar tendon
Metal interference screw
558
-
Biobsorbable interference screw
552
-
Soft tissue (Femoral)
Bone Mulch
TM
Screw (Biomet. Inc.)
1.112
115
EndoButton
®
(Smith & Nephew Endoscopy)
1.086
79
RigidFix
®
(DePuy Synthe)
868
77
SmartScrew
®
ACL (ConDed Linvatec)
794
96
BioScrew
®
(ConMed Linvatec)
589
66
RCI
TM
Screw (Smith & Nephew Endoscopy)
546
68
Soft tissue (Tibial)
Intrafix
®
(DePuy Synthes)
1.332
223
WasherLoc
TM
(Arthrotek)
975
87
Tandem spiked washer (Arthrotek)
769
69
SmartScrew
®
ACL
665
115
BioScrew
®
612
91
SoftSilk
TM
(Acufex Microsurgical. Mansfield, MA)
471
61
Table 2:
From West and coworkers
[5]