J. CHAPPUIS, J. BARTH, J.C. PANISSET
78
metal but are now available in bioabsorbable
material. They have the same initial strength
and ease of insertion but the bioabsorbable
screws have several advantages, including
MRI compatibility, decreased risk of graft
laceration and facilitation of revision surgery.
However, they have also disadvantages,
including screw breakage, foreign body
reaction and increased cost [5].
Cross-pin fixation [6] can be used with results
similar to interference screws but with the risk
of bone plugs fracture if the bone plug size is
less than 9mm.
Suspensory device can also be used.
In Lyon, we like to use the “Chambat” method
which consist of a press-fit fixation without any
material, with good fixation strength [7].
For hamstring and other soft tissue graft, as for
BPTB, you can use suspensory fixation devices,
cross-pin fixation and interference screws.
Endobutton (Smith and Nephew) is a cortical-
based suspensory fixation device that has
enjoyed a great popularity with good
biomechanical results and clinical outcomes
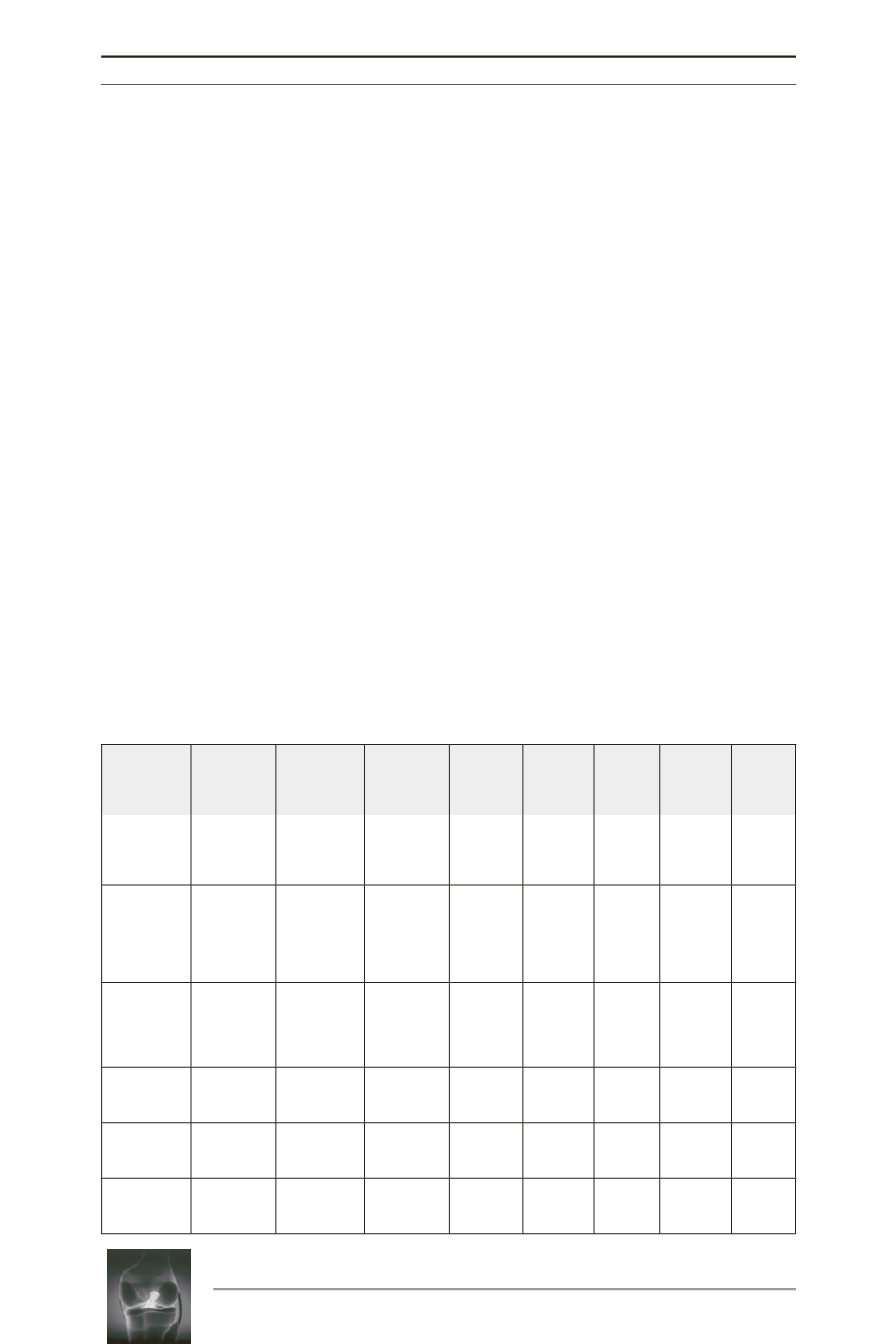
[8] (Table 3). One concern of this device is
widening of the tunnel greater than with
aperture fixation. One hypothesis is more graft-
bone motion known as “bungee-effect” even if
Brown and coworkers showed no difference in
graft-bone motion between suspensory and
aperture fixation in their cadaveric study [8].
New adjustable suspensory devices such as
Tightrope (Arthrex) and Togglelock (Biomet)
seem to have a problem of lengthening greater
than 3mm in a recent study [9].
Cross-pin fixation such as RigidFix (Depuy
Synthes) and TransFix (Arthrex) have shown
similar results compared to the Endobutton [1].
The advantage of suspensory or cross-pin
fixation is a better contact between the graft
and the tunnel.
Variable
Bio-
Interference
Screw
8 X 23mm
EndoButton.
EndoButton
Tape
20mm
EndoButton
Continuous
Loop
20mm
LinX HT
Bone
Mulch
Screw
TransFix PT Screw
7 X 25mm
PT
Suture
Button
Steady-state
graft-
bone motion
(mm)
0.35 ± 0.15
n = 9
0.55 ± 0.17
n = 7
0.51 ± 0.14
n = 7
0.54 ± 0.27
n = 7
0.36 ± 0.08
n = 8
0.44±0.23
n = 9
0.34 ± 0.15
n = 7
0.67±0.17
n = 10
Maximum
Graft-Bone
displacement
after
1.000 cycles
(mm)
4.34 ± 3.16
n = 7
5.82 ± 1.81
n = 7
2.13 ± 0.26
n = 6
2.20 ± 0.95
n = 7
2.24 ± 0.53
n = 7
2.37±1.43
n = 7
1.53 ± 0.42
n = 5
4.42±1.53
n = 8
Graft-bone
displacement
After
20 cycles
(% of max)
42 %
n = 7
79 %
n = 7
72 %
n = 6
71 %
n = 7
70 %
n = 7
59 %
n = 7
62 %
n = 5
75 %
n = 9
Ultimate
failure load
(N)
562 ± 69
n = 9
644 ± 91
n = 10
1.345 ± 179
n = 11
687 ± 129
n = 10
977 ± 238
n = 10
934 ± 296
n = 10
710 ± 224
n = 8
664 ± 132
n = 10
Linear
stiffness
(N/mm)
257 ± 37
n = 9
182 ± 20
n = 10
179 ± 39
n = 11
230 ± 32
n = 10
257 ± 50
n = 10
240 ± 74
n = 10
298 ± 36
n = 8
207 ± 36
n = 10
Displacement
to failure
(mm)
3.00 ± 0.66
n = 9
6.27 ± 2.16
n = 10
9.89 ± 2.41
n = 11
3.74 ± 1.05
n = 10
6.49 ± 2.66
n = 10
7.37 ± 371
n = 10
3.17 ± 0.87
n = 8
6.02±2.47
n = 10
Table 3:
From Brown and coworkers
[8]