
P.R.F. Saggin, P. Ferrua, P.G. Ntagiopoulos, D. Dejour
30
acute dislocations recognition and evaluation
of associated lesions. The acute findings include
[25-28] (fig. 6):
- Lateral femoral condyle contusion and⁄or
osteochondral lesion;
- Medial patellar facet contusion and⁄or
osteochondral lesion, sometimes with
osteochondral fragment avulsion;
- Injury of the medial retinaculum at its patellar
attachments or mid-substance; Tearing of the
distal belly of the
vastus medialis obliquus
;
- Injury of the medial patellofemoral ligament
at its femoral origin;
- Patellar tilt and subluxation;
- Joint effusion.
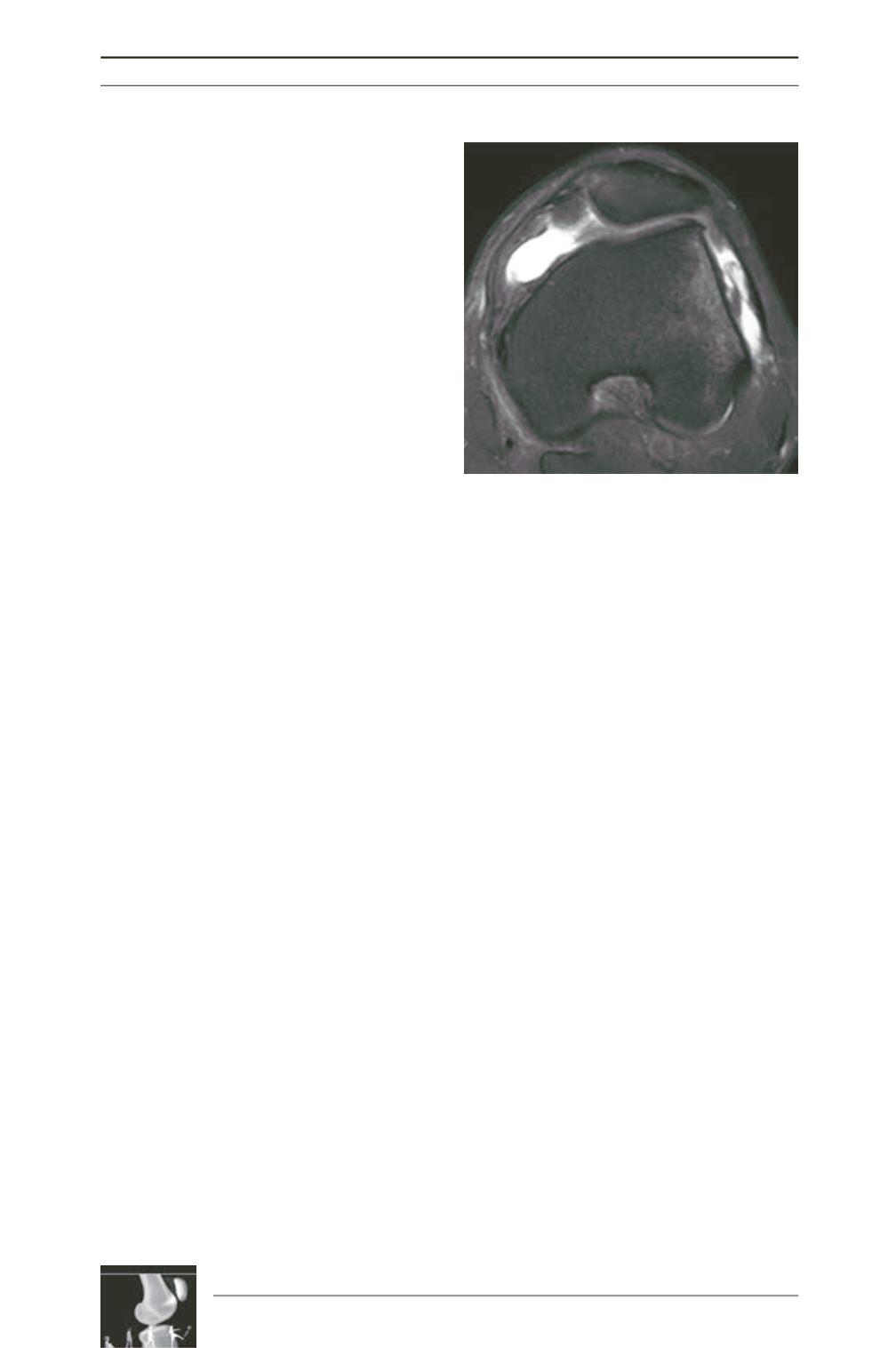
Fig. 6: MRI performed after acute dislocation. The
medial retinaculum is torn and contusions of the
medial patellar facet and lateral condyle are
evident.
Literature
[1] Dejour H, Walch G, Nove-Josserand L,
Guier C. Factors of patellar instability: an anatomic
radiographic study.
Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.
1994; 2(1): 19-26.
[2] Maldague B, Malghem J. Significance of the
radiograph of the knee profile in the detection of patellar
instability. Preliminary report.
Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice
Appar Mot. 1985;71 Suppl 2: 5-13.
[3] Dejour D, Reynaud P, Lecoultre B. Douleurs
et instabilité rotulienne, Essai de Classification.
Médecin et
Hygiène. Juillet. 1998; 1466-71.
[4] Dejour D, Saggin P. The sulcus deepening
trochleoplasty-the Lyon’s procedure.
Int Orthop. 2010 fev;
34(2): 311-6.
[5] BRATTSTROEM H. Shape of the Intercondylar Groove
Normally and In Recurrent Dislocation of Patella. A Clinical
And X-Ray-Anatomical Investigation.
Acta Orthop Scand
Suppl. 1964;68: Suppl 68: 1-148.
[6] Merchant AC, Mercer RL, Jacobsen RH,
Cool CR. Roentgenographic analysis of patellofemoral
congruence.
J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974 out; 56(7): 1391-6.
[7] Davies AP, Bayer J, Owen-Johnson S,
Shepstone L, Darrah C, Glasgow MM,
et al.
The
optimum knee flexion angle for skyline radiography is thirty
degrees.
Clin Orthop Relat Res 2004 jun;(423): 166-71.
[8] Stäubli HU, Dürrenmatt U, Porcellini B,
Rauschning W. Anatomy and surface geometry of the
patellofemoral joint in the axial plane.
J Bone Joint Surg Br.
1999 maio; 81(3): 452-8.
[9] Carrillon Y, Abidi H, Dejour D, Fantino O,
Moyen B, Tran-Minh VA. Patellar instability:
assessment on MR images by measuring the lateral trochlear
inclination-initial experience.
Radiology 2000 ago; 216(2):
582-5.
[10] Dejour D, Le Coultre B. Osteotomies in patello-
femoral instabilities.
Sports Med Arthrosc 2007 mar;15(1):
39-46.
[11] Lippacher S, Dejour D, Elsharkawi M,
Dornacher D, Ring C, Dreyhaupt J,
et al.
Observer
Agreement on the Dejour Trochlear Dysplasia Classification:
A Comparison of True Lateral Radiographs and Axial
Magnetic Resonance Images.
The American Journal of
Sports Medicine [Internet]. 2012 jan 11 [citado 2012 fev
12];
Available
de:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22238057.
[12] Caton J. Method of measuring the height of the
patella.
Acta Orthop Belg. 1989; 55(3): 385-6.
[13] Caton J, Deschamps G, Chambat P, Lerat
JL, Dejour H. Patella infera. Apropos of 128 cases.
Rev
Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1982; 68(5): 317-25.











