D. Saragaglia, M. Blaysat, M. Grimaldi
152
Drawing on our experience with TKR and HTO
navigation [15, 19, 20] we used the principles
of computer-assisted surgery for double level
osteotomy (DLO) hoping to increase the
accuracy of this difficult procedure. Our
experience is based on 72 DLO performed
between August 2001 and June 2014, out of
600
personal
computer-assisted
knee
osteotomies for genu varum deformities (12%).
The objective of this article is to present
the clinical and radiological results of the
first 42 patients at a mean follow-up of
46 ± 27 months.
Materialand methods
The series was composed of 38 patients
(4 bilateral), 9 females and 29 males aged from
39 to 64 years (mean age: 50.9 ± 7.1 years). We
operated on 22 right knees and 20 left ones.
The mean BMI was 29.3 ± 4.3 for a mean
height of 171cm and a mean weight of 85.8kg.
For functional assessment, we used the
Lysholm-Tegner score [25] to evaluate patients,
both pre-operatively as post-operatively. We
felt this scoring system was better adapted than
the IKS score usually used to evaluate surgical
treatment for knee osteoarthritis. The mean
score was of 41.2 ± 8.9 points (22-69).
According to modified Ahlbäck criteria [21],
we operated on 9 stage 2, 25 stage 3, 7 stage 4
and 1 stage 5. We measured HKA (Hip-Knee-
Ankle) angle using Ramadier’s protocol [16]
and we also measured the medial distal femoral
mechanical axis (MDFMA) and the medial
proximal tibial mechanical axis (MPTMA) to
pose the right indication [23]. These measures
were respectively: 167.7° ± 3.5° (159°-172°),
87.28° ± 1.41° (83°-90°) for the MDFMA and
83.51° ± 2.7° (78°-88°) for the MPTMA.
The inclusion criteria were a patient younger
than 65 years old with a severe varus deformity
(more than 8° - HKA angle ≤ to 172°) and a
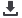
MDFMA at 91° or less (fig. 2).
All the osteotomies were navigated using the
O
rthopilot
® device
(B-Braun-Aesculap,
Tuttlingen, Germany)
. The procedure was
performed as described previously [23]: after
inserting the rigid-bodies and calibrating the
lower leg, we did first the femoral closing
wedge osteotomy (from 4 to 7mm) which was
fixed by an AO T-Plate, and secondly, after
checking the residual varus, the tibial opening
wedge osteotomy using a B
iosorb
® wedge
(β Tricalcium phosphate, SBM, Lourdes,
France) and a plate (AO T-plate or C-plate).
The goals of the osteotomy were to achieve an
HKA angle of 182° ± 2° and a MPTMA angle
of 90° ± 2°.
The functional results were evaluated not only
according to the Lyshölm-Tegner score [25]
but also to the KOOS score [18]. The patients
answered the questionnaire at revision or by
Fig. 2: Severe genu varum deformity with MDFMA
at 87.8°, MPTMA at 80.4° and HKA angle at 168°.