147
Introduction
High tibial osteotomy (HTO) is a surgical
technique that gives good results in the manage
ment of degenerative osteoarthritis of the knee
with frontal distortion in genu varum [1, 2].
Two main surgical procedures predominate:
opening wedge (OWHTO) and closed wedge
high tibial osteotomy (CWHTO).
According to the literature, the first has one
well-known side effect: The increase in the
tibial slope [3-6], which is responsible for
increased strain in the anterior cruciate
ligament [7].
Nevertheless, we put forward the hypothesis
that the tibial slope can be modified by the
positioning of the wedge and especially that
posterior positioning can limit this side effect.
Materials and methods
This study involved 141 patients operated on
by a single surgeon (GD) between March 2007
and November 2009. For each patient, opening-
wedge high tibial osteotomy (OWHTO) was
performed for medial degenerative osteo
arthritis of the knee. No exclusion criteria were
used.
Tibial slope and osteotomy:
technical aspects
S. Tomes, G. Deschamps
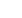
Fig. 1: Posterior tibial slope measurement
(Brazier et al.)