S. Tomes, G. Deschamps
148
X-rays were done for each patient (full-length
anterior-posterior weight-bearing view, a.p.
knee X-ray and knee in profile) three times: At
the pre-operative time, at the fifth day after
surgery and at the last follow-up.
The tibial slope was measured on the knee in
profile X-rays with the cortical posterior
reference described by Brazier
et al.
[8].
Each patient was assessed with the Knee
Society Score (KSS) [9], pre-operatively and at
the last follow-up.
Surgical technique for
opening wedge high
tibial osteotomy
The patient is in the supine position, with knee
flexion around 90 degrees and a tourniquet.
The approach is medial through an eight-
centimeter incision.
The medial collateral ligament (superficials
fibers) is cut perpendicularly to the major axis.
Beforehand, we have detached the pes anserinus
from its insertion and retracted it, the cut
forming a reversed L. The pes anserinus is used
to cover the plate at the end of the surgery. A
scaler is used to free the soft tissue at the
posterior part of the tibia. Posterior blood
vessels and the patellar tendon are protected by
two retractors. Then an oblique osteotomy is
performed with an oscillating saw, completed
with a chisel (to cut through the posterior cortex
of the bone completely). The osteotomy is then
opened and a trial wedge is positioned. Then,
the final wedge (we use a bone bank wedge) is
put in place. To position thewedge as posteriorly
as possible, the posterior part of the wedge is
positioned parallel to the posterior part of the
cortical bone.
It is important to remember two essential
elements: First, it is necessary to cut the
posterior part of the cortical bone completely
and second, it is important to position the final
wedge parallel to the posterior tibial cortex.
The final part of this surgery is the fixation of
the osteotomy with a plate. We used the
Activmotion plate (N
ewclip
®).
Statisticalanalysis
The various values of tibial slope and KSS
score were compared using the bilateral paired
parametric Student test (p<0.05) when the
distribution was normal.
Results
In this study, the mean follow-up was
42.7 months (26-65), the mean age was
56.6 years (28-73), the sex-ratio was 3.8 M/1 F,
and the mean BMI was 26.5 kg/m
2
(18.9-40.4).
The mean pre-operative medial tibial slope
was 5.4° (-2-13), 5.8° (-2-12) at the 5
th
day and
5.8° (-2-12) at the last follow-up. There was no
statistically significant difference (p=0.8).
Concerning the clinical assessment, The
International Knee Society Score results varied
from 127.7 to 186.1 and the difference was
statically significant (p<0.001).
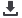
Fig. 2: Profile view of osteotomy (The retractor is
posterior). The final wedge is posterior and the
posterior gap is larger than the anterior.