Custom anatomic CR TKR
93
Variable thick medial and lateral inserts allow a
90 degree cut perpendicular to the tibial
mechanical axis, but restore proximal tibial
anatomy.
Restauration of the distal femoral condylar
anatomy and proximal tibial joint line restore
and correct the limb malalignment (fig. 4).
Rotation of the femoral component is based on
the restoration of medial and lateral J-curves.
The rotation of the tibial component is designed
using the Cobb’s method [4] but slight
undersizing allows correction of rotation if
necessary following either the position of the
tibial tray during range of motion or orienting
the component toward the tibial tubercle as
recommended by Lawrie
et al.
[9].
Early clinical results report less blood loss,
bone preservation.
Early cadaveric kinematics studies confirm the
hypothesis that restoration of the distal femur
and proximal tibia resemble more closely
normal knee knee kinematics compared to off-
the-shelf implants comparing knee kinematics
before and after surgery [10].
Early clinical results are encouraging and report
less bone resection, less ligament releases and
good mechanical alignment [11-13].
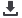
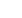
Fig. 4 a and b: In custom TKR the distal femoral condylar geometry is restored and based on a perpendicular
cut of the tibia the space on the lateral side is filled with polyethylene to restore overall alignment.
Literature
[1] Mahoney OM, Kinsey T. Overhang of the femoral
component in total knee arthroplasty: risk factors and clinical
consequences.
J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010; 92(5): 1115-21.
doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.00434.
[2] Bedard M, Vince KG, Redfern J, Collen SR.
Internal rotation of the tibial component is frequent in stiff
total knee arthroplasty.
Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011; 469(8):
2346-55. doi:10.1007/s11999-011-1889-8.
[3] Nicoll D, RowleyDI. Internal rotational error of the
tibial component is a major cause of pain after total knee
replacement.
The Journal of bone and joint surgery British
volume. 2010; 92(9): 1238-44. doi:10.1302/0301-
620X.92B9.23516.
[4] Cobb JP, Dixon H, Dandachli W, Iranpour F.
The anatomical tibial axis: reliable rotational orientation in
knee replacement.
The Journal of bone and joint surgery
British volume. 2008; 90(8): 1032-8. doi:10.1302/0301-
620X.90B8.19905.
[5] Hunter DJ, Niu J, Felson DT,
et al.
Knee alignment
does not predict incident osteoarthritis: the Framingham