SINGLE-BUNDLE ACL RECONSTRUCTION: HOW I DO IT
145
DRILLING THE ACL
FEMORAL TUNNEL
• Desired femoral tunnel location marked with
a microfracture awl;
• ACL femoral tunnel drilled in hyperflexion;
• More flexion = longer femoral tunnel;
• Angling the guide pin more laterally increases
the obliquity of the tunnel and increases the
femoral tunnel length.
DRILLING THE ACL TIBIAL
TUNNEL
• View the ACL tibial attachment site through
the AM portal. This approach positions the
arthroscope directly over the ACL tibial
attachment site resulting in an orthogonal
view. This view allows for more accurate
assessment of the guide pin location within
the ACL tibial attachment site in both the
anterior-posterior
and
medial-lateral
directions.
• ACL tibial guide inserted through the AAM
portal. This positions the arm of the aimer
parallel to the joint line.
• Tibial guide pin positioned anterior to the
posterior border of the lateral meniscus and
as far medially in the footprint as possible.
• The tibial aimer bullet is marked with a
surgical marker at the desired tibial tunnel
length.
• The tibial aimer arm is raised or lowered until
the marked position on the aimer bullet
contacts the end of the aimer handle when the
bullet is flush with the anterior cortex of the
tibia.
Fig. 14:
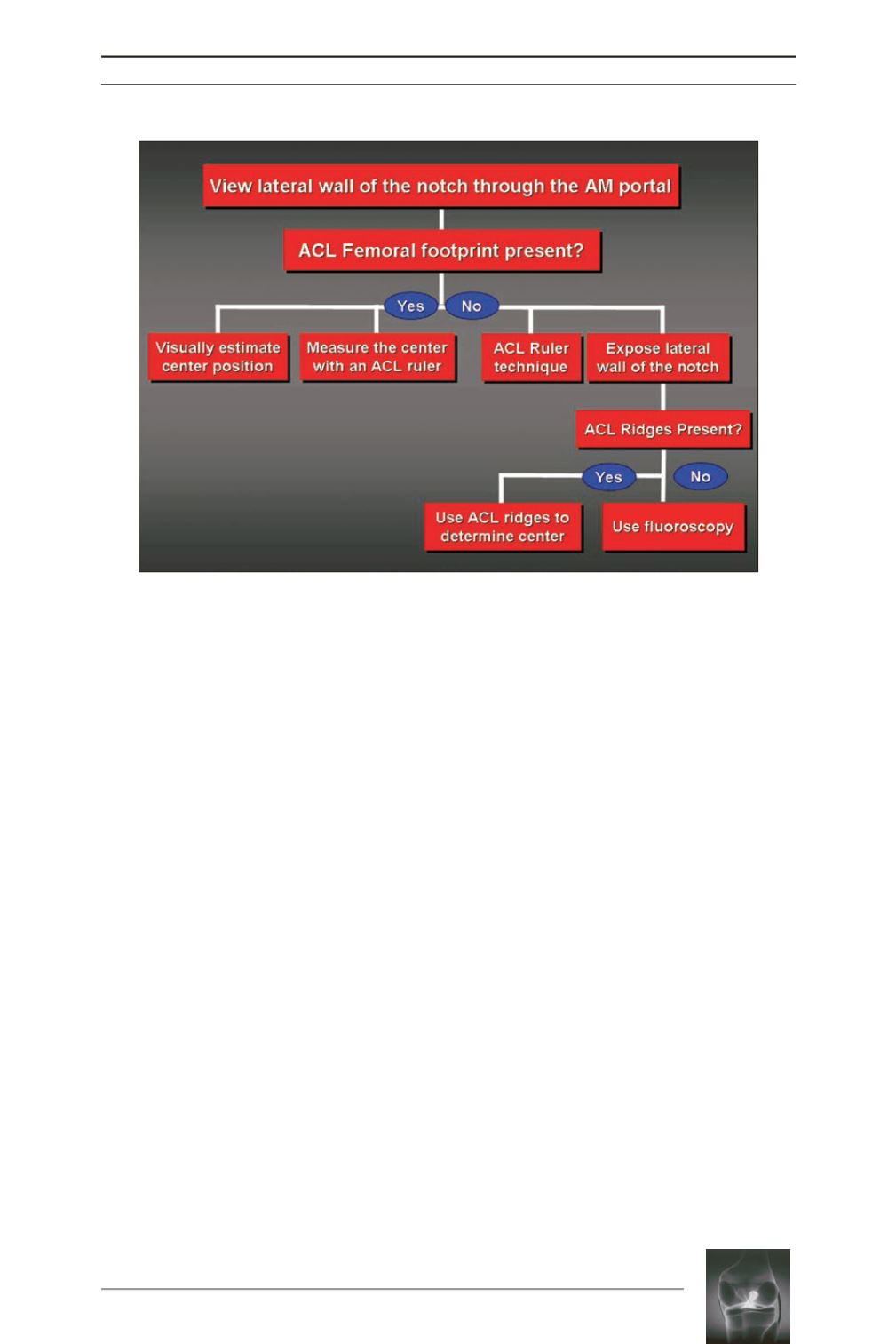
Algorithm for ACL femoral tunnel placement.