to avoid because femoral component flexion
together with a pronounced posterior slope of
the tibia might allow for impingement even
with little or no clinical hyperextension [17].
The tibial post is particularly vulnerable to
wear from rotational malalignment between
femur and tibia [17]. According to anterior
impingement a more anterior placement of the
post on the tibial plateau adversely effects
polyaethylene wear and damage [5]. Amount
of wear and location of tibial post damage
again are design dependant and can occur on
the anterior and posterior flanges but as well
on the medial and lateral surfaces of the post as
shown in retrieval studies [11].
FURTHER DIRECTIONS
IN POSTERIOR
STABILIZATION
If the problems of dislocation and post wear
could be solved, the concept of posterior stabi-
lization would become even more attractive
because it allows for guided motion of the
prosthetic knee in a more natural fashion.
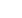
Optimal dislocation safety respecting the dis-
location safety factor is probably the number
one requirement when introducing a new PS
design (fig. 5). Increased contact area for the
post-cam mechanism and a rounded post to
allow for rotational freedom theoretically
reduce post wear and damage. New materials
might offer higher stability and better wear
resistance [9]. Mobile plateau posterior stabili-
zed knees have been shown to reduce contact
stress of the post-cam mechanism [16]. The bi-
cruciate stabilized knee is still experimental
[18]. Perfect alignment of long bone axes and
restoration of correct femorotibial rotation are
still mainstays to avoid component and post
overload.
Whereas for the purpose of this article the post
box part of the PS-knee has been described
isolated from the rest of the prosthesis it has to
be kept in mind that the post and box are func-
tioning as a unit together with the other parts
of the components and are dependant from the
condylar and tibial geometry.
14
es
JOURNÉES LYONNAISES DE CHIRURGIE DU GENOU
208
Fig. 5 : The dislocation safety factor (DSF)
was defined as the vertical distance from the
tip of the post to the inferior border of the
cam
(G
EMINI
SL®, Link, with permission).