ventional instrumentation and less experienced
with navigation carried on TKA.
Surgical procedure and follow-up
Conventional instrumentation used intrame-
dullary roding for the femur and extramedul-
lary instrumentation jig for the tibia. The
femur was externally rotated by three degrees
using distal femoral jig. No patella resurfacing
was performed in any conventional and navi-
gated knees. Closure was done in three layers
and a dry dressing covered the wound as well
as a compressed bandage the patient kept for
24 hours.
Navigation instrumentation used an optoelec-
tronic tracking system (Stryker Vision™ or
OrthoPilot™) and integrated jigs equipped
with LED trackers. After knee approach the
surgeon had to register the lower limb accor-
ding to CTfree navigation concepts and com-
pany recommendations. Therefore the sur-
geons used equipped instrumentations to align
the femur and the tibia 90 degrees to the
respective mechanical axes. Femoral rotation
was set with respect to the average of transepi-
condylar and posterior condylar axes.
Postoperative care and follow-up
The physiotherapy and ergotherapy protocols
were the same both conventional and naviga-
ted knees including early mobilisation with
full weight bearing using either a Zimmer
frame, crutches or sticks. Post operative care
was standardized and patients were mobilized
early and discharged when filling indepen-
dence and mobility criteria.
Patients were reviewed after 6 weeks and one
year by the Arthroplasty Service and data col-
lection such as ROM, Oxford Score were
stored on our database system.
Gait analysis protocol
Patients underwent gait assessment and analy-
sis at a range of 6 to 14 months after surgery
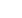
(mean 8 months) (fig. 1 Patient set up). Using
an 8-camera Vicon™ motion analysis system
set at 120Hz (real-time motion) (fig. 2 Camera
set up).
Sets of 14mm reflective markers were placed
on the first and the fifth metatarsal as well as
on the medial and lateral malleoli and the heel.
Cluster markers (set of four arranged in a
rhombus formation) were placed on the thigh
and on a waist band.
After a calibration step so-called static and
dynamic trials, each subject performed several
test trials prior to recording testing to familiar-
ize with the series of exercises and trials. Three
series of data were collected stored and ana-
lyzed. The following functional activities were
assessed: walking, rising from/sitting in chair,
and ascending/descending stairs. Functional
outcome measures were temporospatial
ANALYSE À LA MARCHE DE DEUX SÉRIES HOMOGÈNES DE 40 PATIENTS OPÉRÉS DE PTG…
251
Fig. 1: Gait analysis.
Patient equipped with trackers.
Fig. 2: Camera set up for gait analysis.