Postoperatively, the mean loss of extension
was 0.4° ± 1 (0-7) and 0.6° ± 2 (0-10) (p=0.6)
in the study group and the control group, res-
pectively. The mean flexion was 122° ± 11
(95-140) and 120° ± 13 (85-140) (p=0.3). The
mean IKS knee score was 95 ± 6 (74-100) and
93 ± 8 (67-100) (p=0.1). The mean IKS func-
tion score was 83 ± 19 (20-100) and 84 ± 16
(50-100) (p=0.7). No patient in the study
group underwent revision knee arthroplasty.
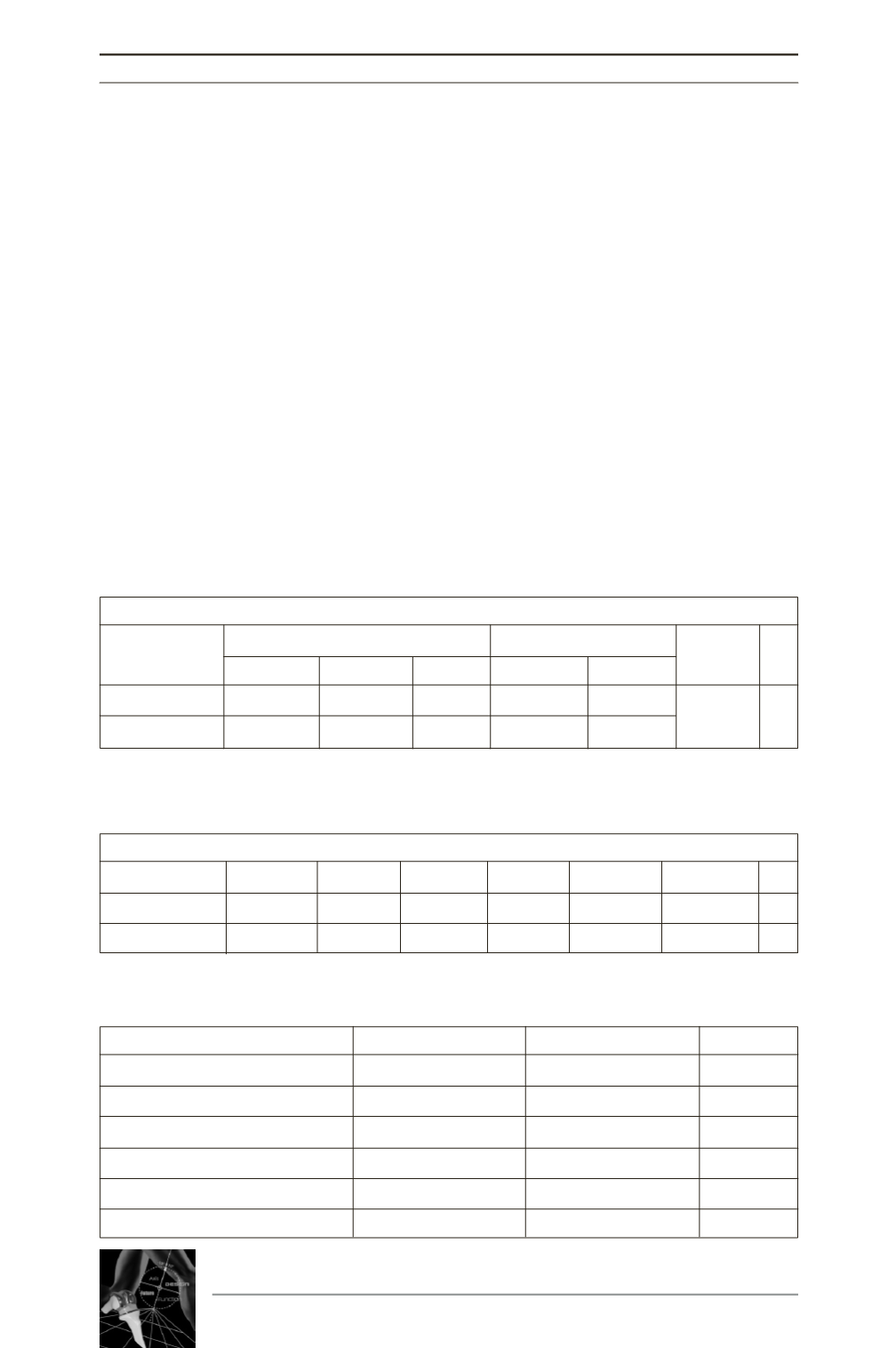
A tibial radiolucent line (RLL) was observed
in 11 cases of the study group and 7 cases of
the control group (p=0.3). These RLL showed
no progression in both groups. There was no
suspicion of aseptic loosening (Table 1).
On a lateral view, a femoral RLL was observed
in 8 cases in each group (p=1). There was no
suspicion of aseptic loosening of the femoral
component (Table 2).
There was no significant difference in terms of
restitution of mechanical axis (Table 3).
DISCUSSION
The current recommendation for a clinically
unstable knee with an isolated ACL rupture is
that reconstruction should not be delayed
unnecessarily so as to avoid secondary menis-
14
es
JOURNÉES LYONNAISES DE CHIRURGIE DU GENOU
310
Tibial Radiolucent Lines
AP View
Lateral View
Incidence P
Zone 1-2 Zone 3-4 Zone 7 Zone 1 Zone 2
Study group
10
6
1
2 2
11
0.3
Control group
7
0
0
0 1
7
Table 1 : TIbial radiolucent lines
Femoral Radiolucent Lines
Zone 1 Zone 2 Zone 3 Zone 4 Zone 5-7 Incidence P
Study group
3
0
0
8
0
8
1
Control group
5
1
2
4
0
8
Table 2 : Femoral radiolucent lines
Study group
Control group
P
HKA shaft (°)
179 ± 3
178 ± 3
0.2
Femoral mechanical axis (°)
89.5 ± 1.6
88.8 ± 2.3
0.1
Tibial mechanical axis (°)
89.4 ± 2
89.3 ± 1
0.9
Blackburne index
0.6 ± 0.2
0.65 ± 0.2
0.7
Slope (°)
88.6 ± 2.5
89 ± 2
0.8
Tibial translation (mm)
0.4 5
0 ± 4
0.7
Table 3 : Postoperative radiological assessment