
Minimal invasive reconstruction of the MPFL using Quadriceps tendon
141
The graft is left attached distally and the free
proximal end is armed with resorbable sutures
in web stitch technique.
Distally the longitudinal cuts are continued
with a surgical knife towards the patella and
over the patellar surface in the chosen width
(10 or 12mm) (Lateral: 2cm, medial: 1cm on
the surface of the patella). The quadriceps
tendon strip is than subperiostally elevated
from the surface of the patella.
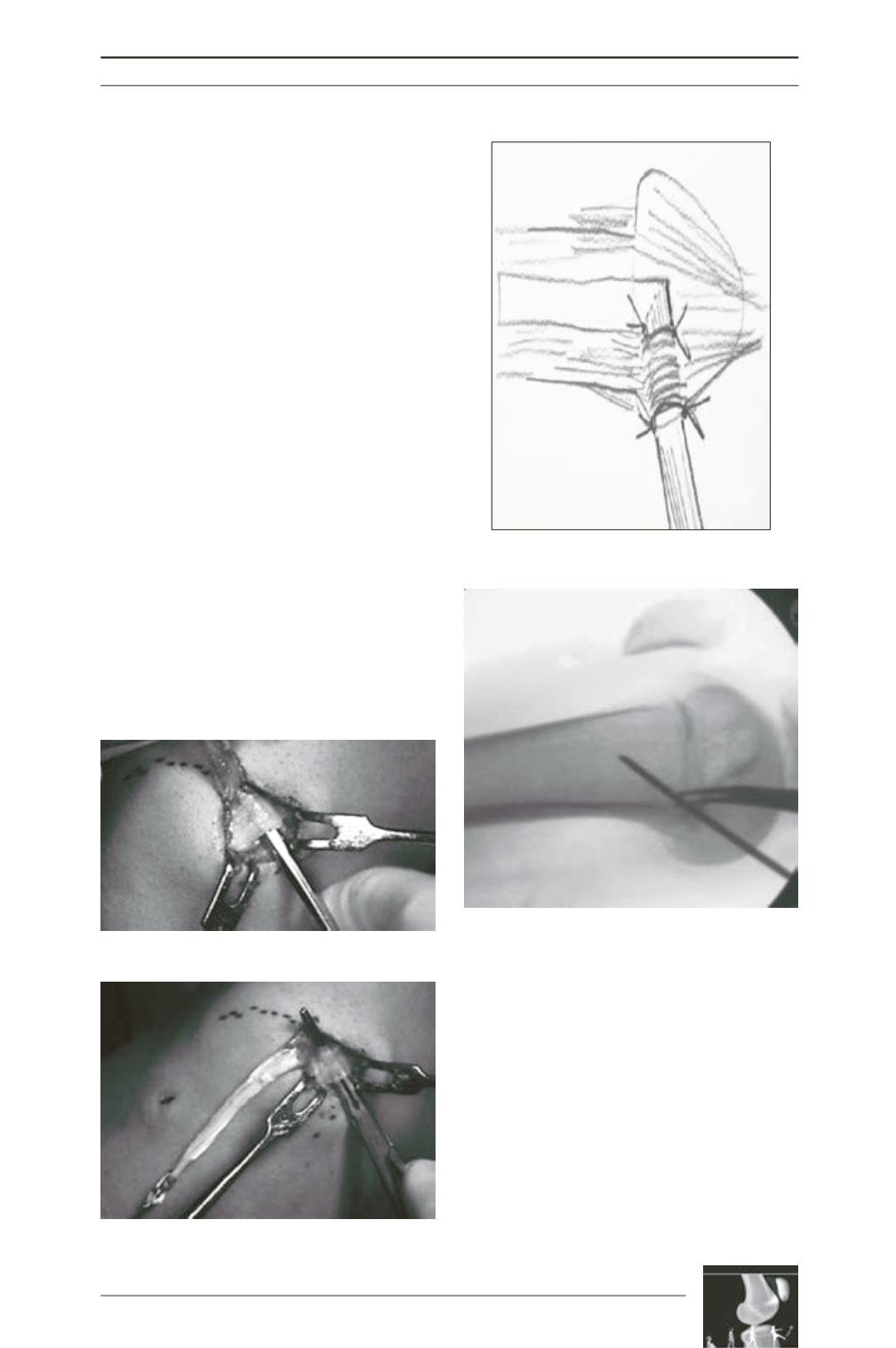
The proximal 1.5cmof the medial patellar border
is then exposed. From the medial patella border
the prepatellar tissue is elevated towards laterally
creating a tunnel reaching the medial edge of the
graft. This is performed best with a periostial
elevator (fig. 7) ), so that anterior cortex of the
patella in the tunnel is gently abraded. A surgical
clamp is introduced into the tunnel from medial
to lateral and the graft is passed through the
tunnel (fig. 8). The graft pulled through the
tunnel should lie flat on the abraded cortex of the
patellar surface, so that fast and broad graft-to-
bone healing can be expected. The graft is then
secured to the retinaculum tissue on the medial
patellar edge by resorbable sutures (fig. 9).
A 1.5cm skin incision is then made over the
adductor tubercle. Starting at the patella a
curved clamp is used to create a tunnel in the
space between the vastus medialis and the
capsule. A suture loop is then pulled through
the tunnel. This loop is used later to pull the
graft towards the femoral insertion.
Under fluoroscopic guidance a 2.4mm guide
pin is drilled into the insertion of the MPFL [8].
It is directed antero-laterally to exit the femur
Fig. 7
Fig. 8
Fig. 9
Fig. 10











