
Whether to resurface the patella in total knee arthroplasty
339
Photographs under arthroscopy were taken
once the femoral and tibial implants were
cemented. This arthroscopy is performed
without water, in order not to compromise the
coupling between the non-resurfaced patella
and the femoral plate. The arthroscope was
passed via an anteromedial portal with the knee
at 45° of flexion.
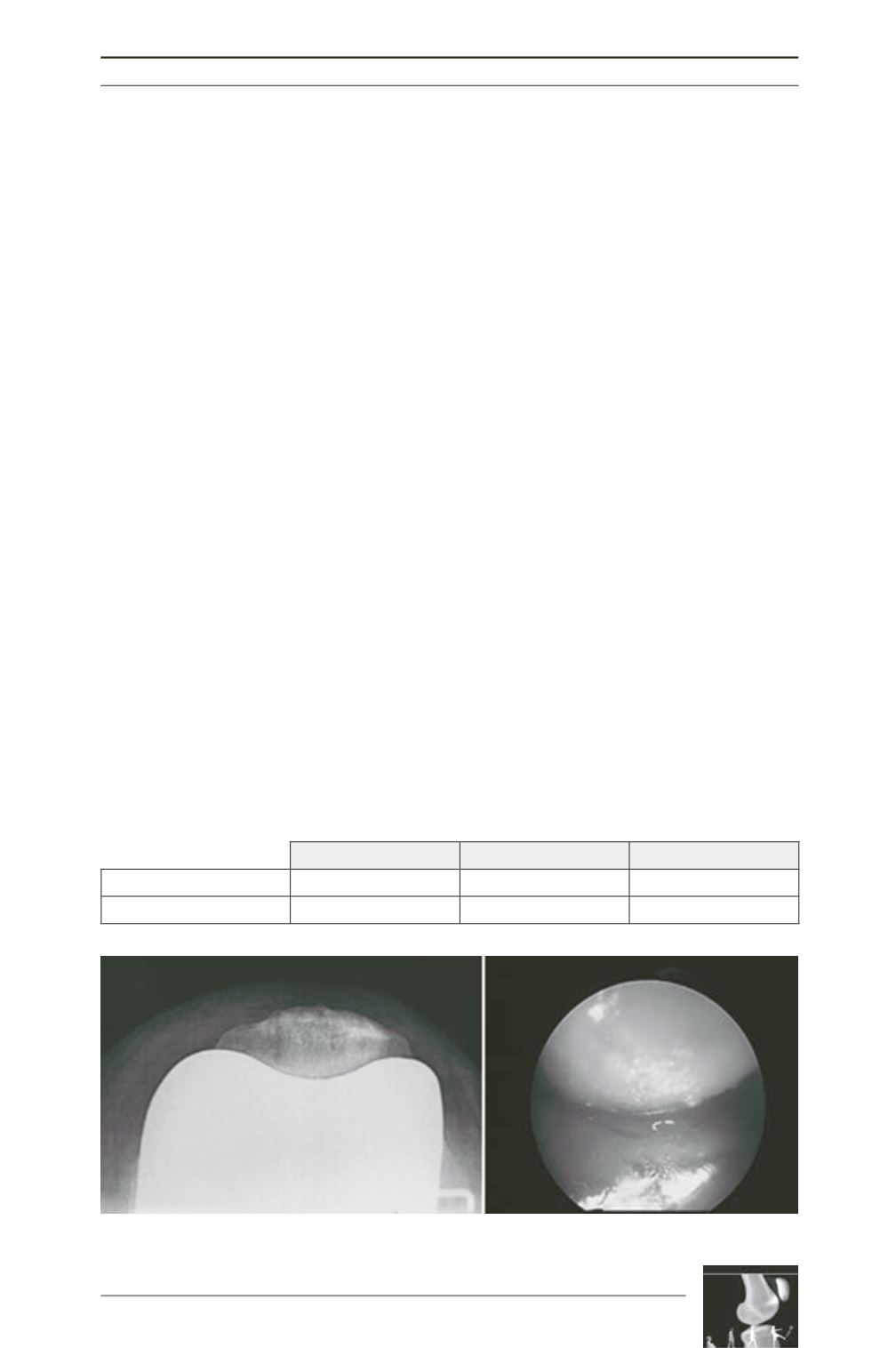
For characterisation of patellofemoral con
gruency, both arthroscopic and radiological
congruencies were taken into account. The
arthroscopic images were analysed according
to whether or not the patellar surface was in
contact with the entire centre of the trochlear
groove in the knee at 45° of flexion, the
radiographs according to alignment and the
overall contact surface of the patella.
Arthroscopic congruency was defined as a
harmonious contact of the patella with the
entire trochlear groove, radiographic con
gruency, as a harmonious contact of the patella
with the entire femoral plate.
A patellofemoral pair was only considered
congruent if, and only if, congruency was
simultaneously found in the arthroscopic
images and the radiographic examination.
At the end of this analysis, each patellofemoral
pair was then classified into 2 groups: congruent
and non-congruent.
The patients were reviewed again at 1 year,
with a clinical and radiological evaluation.
The evaluation at 1 year included the Knee
Society score, the presence of anterior pain
syndrome, the presence of patellofemoral
syndrome, a global evaluation of satisfaction
(“very satisfied”, “satisfied”, “not very
satisfied”, “dissatisfied”).
A Fisher test was used for evaluation of
significance of the results.
Results
Out of the 17 knees included, 12 presented as
congruent patellofemoral pairs and 5 as non-
congruent (fig. 4a, b).
Among these 5 non-congruent pairs, 2 patellae
were classed as Wiberg 2, and 3 as Wiberg 3
(table 1).
Wiberg 1 =4/17
Wiberg 2 =8/17
Wiberg 3 =5/17
Congruent = 12/17
4
6
2
Non-congruent = 5/17
0
2
3
Table 1
Fig. 4a: Congruent patellofemoral pair: radiographic and arthroscopic.











