undergoing TKA. We therefore decided to
investigate this in a cohort of 1000 consecutive
patients undergoing TKA. Our hypothesis was
that both gender and morphotype determine the
shape of the knee in patients undergoing TKA.
MATERIALS AND
METHODS
A cohort of 1000 consecutive patients that
underwent a primary total knee arthroplasty
for end stage knee pathology at our institution
were included into this prospective study. All
patients were operated between April 2003 and
June 2007 and received a pre- and postoperati-
ve CT-scan of the distal femur and proximal
tibia, as well as calibrated full leg radiographs
with full pelvic views as part of the prospecti-
ve protocol. Patients that underwent a bilateral
TKA were included only once, regardless
whether the surgery was performed as a one-
or two-stage procedure. Patients with previous
ipsilateral unicondylar or patellofemoral
arthroplasty were excluded, as well as patients
of non Caucasian race.
686 Patients were female, 314 were male. The
average age of the male patients was 66 ± 9.5
years (range 34 to 84 years) and 68,4 ± 10,5
years (range 36 to 89 years) for the female
patients.
In all patients a CT-scan of the distal femur
and proximal tibia was taken the day prior to
the operation, as well as a calibrated standing
full leg radiograph of both legs, including a
full view of the pelvis. CT images were taken
with 2mm slices at the level of the distal
femur, and of these slices the section through
the deepest part of the medial epicondylar sul-
cus was used for the following measurements
of the distal femoral geometry: distal femoral
width at the level of the epicondyles (AB), dis-
tal femoral width at the level of the centre of
the posterior condyles (CD), distal femoral
width at the level of the trochlea (EF), height
of the lateral femoral condyle (CE), and height
of the medial femoral condyle (DF).
14
es
JOURNÉES LYONNAISES DE CHIRURGIE DU GENOU
152
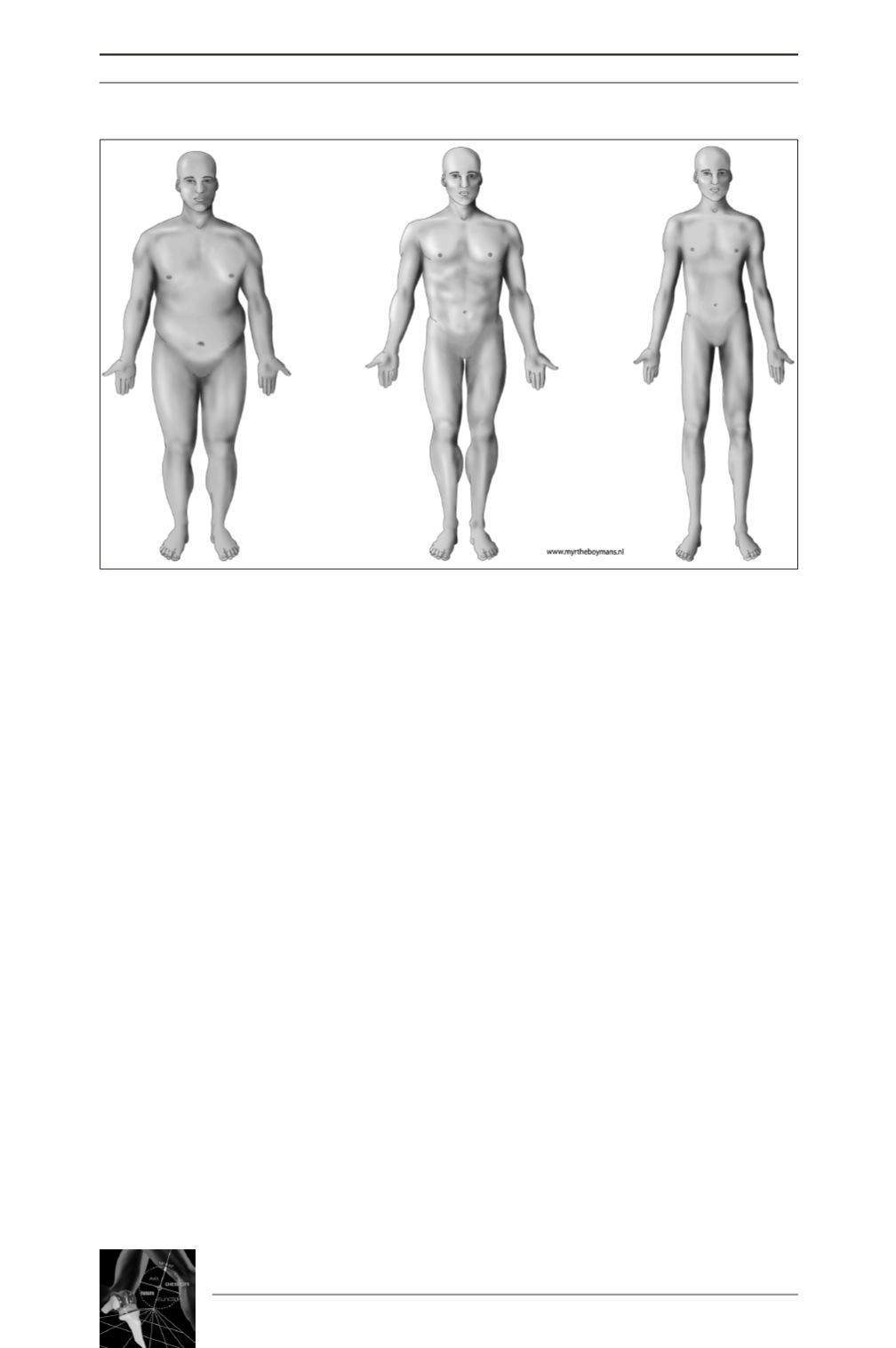
Fig. 1 : The three different morphotypes;
endomorph (left), mesomorph (middle), and ectomorph (right).