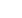
24 succès (68,6 %) sur 35 reprises itératives
pour sepsis. Dans 50 % des cas de notre série,
une arthrodèse a été réalisée. Dans la plupart
des cas (7/8), une guérison du sepsis a pu être
obtenue.
CONCLUSION
L’objectif de cette étude était d’évaluer les
résultats des prises en charge de prothèses du
genou pour infection, en considérant la guéri-
son ou non et le résultat fonctionnel. Dans cette
série, 76 % des patients porteurs d’une prothè-
se du genou de première intention opérés en
2 temps ont présenté une guérison de leur sep-
sis. Le traitement associant une arthrotomie-
lavage-changement du polyéthylène est peu
retenu dans notre service car nous considérons
qu’une infection est une complication grave,
nécessitant une attitude agressive. Devant un
sepsis itératif après échec d’un changement en
deux temps, la possibilité d’une réimplantation
est le plus souvent compromise.
14
es
JOURNÉES LYONNAISES DE CHIRURGIE DU GENOU
286
RÉFÉRENCES
[1] GARDNER J, GIOE TJ, TATMAN P. Can This
Prosthesis Be Saved? Implant Salvage Attempts in Infected
Primary TK.
Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010.
[2] GARVIN KL, CORDERO GX. Infected total knee
arthroplasty: diagnosis and treatment.
Instr Course Lect.
2008 ; 57 : 305-15.
[3] HALEEM AA, BERRY JD, HANSSEN AD. Mid-term
to longterm follow-up of two stage reimplantation for infec-
ted total knee arthroplasty.
Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;
428: 35-9.
[4] MAHESHWARI AV, GIOE TJ, KALORE NV a
nd al.
Reinfection After Prior Staged Reimplantation for Septic
Total Knee Arthroplasty: Is Salvage Still Possible?
J Arthroplasty. 2010 Jun 10.
[5] MAUERHAN DR, NELSON CL, SMITH DL
and al.
Prophylaxis against infection in total joint arthroplasty. One
day of cefuroxime compared with three days of cefazolin.
J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994 ; 76 :39.
[6] MONT MA, WALDMAN BJ, HUNGERFORD DS.
Evaluation of preoperative cultures before second-stage
reimplantation of a total knee prosthesis complicated by
infection. A comparison-group study
. J Bone Joint Surg Am.
2000; 82: 1552-7.
[7] MORTAZAVI SM, SCHWARTZENBERGER J,
AUSTIN MS
and al.
Revision total knee arthroplasty infec-
tion: incidence and predictors.
Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010
; 468(8) : 2052-9.
[8] SUAREZ J, GRIFFIN W, SPRINGER B, FEHRING T
and al.
Why do revision kne arthroplasties fail?
J Arthroplasty. 2008; 23(Suppl 1): 99-103.
[9] TRAMPUZ A, PIPER KE, JACOBSON MJ
and al.
Sonication of removed hip and knee prostheses for diagno-
sis of infection.
N Engl J Med. 2007; 357: 654-63.