
M. Thaunat, C. Bessiere, N. Pujol, P. Boisrenoult, P Beaufils
202
Thus, TT-TG distance and Caton-Deschamps
index were addressed if outside the normal
range; this included TT distalization for
functional patella alta if the Caton-Deschamps
index was greater than 1.2 and TTmedialization
in case of lateral patellar maltracking angle or
when tuberosity offset from the trochlear
groove was greater than 20 mm. MPFL
reconstruction was also performed in case of
increased lateral patellar mobility with positive
apprehension test or in case of abnormal
patellar tilt (greater than 20°) on CT. The lateral
retinaculum was exposed, and resected with a
10 blade. The synovium was excised and all
additional tethering tissue was released
proximally and distally. The method for
determining correction angle and wedge size
included a pre-operative radiological plan
and intra-operative measurement (fig. 3).
Osteotomies were drawn on the bone with a
dermographic pen according to the pre-
operative plan. The anteroposterior cut was
performed first, using a reciprocal saw. Then
the posterior cut was made, strictly parallel to
the frontal plane of the femur, from the lateral
side, and directed medially; it was found safer
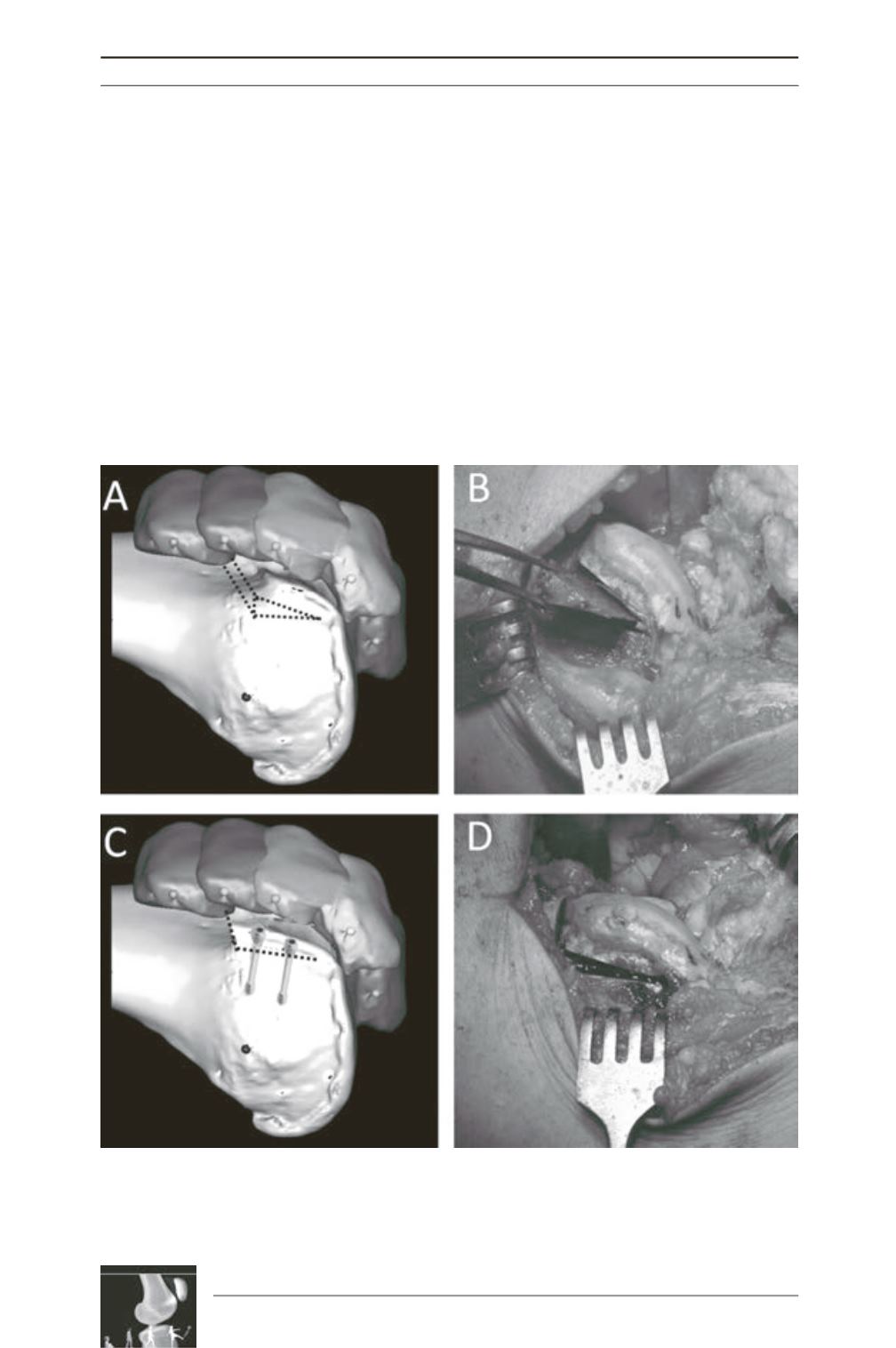
Fig. 3: Recession wedge trochleoplasty surgical technique. 3A and 3B: The base of the wedge which is
removed should be the same in millimeters as the value of the trochlear bump, in order to allow the
trochlea to settle into a deeper position, without modifying the trochlear groove. 3C and 3D: Correction is
obtained after removal of the proximally based wedge by progressively applying pressure on the trochlea.
Fixation uses two 3.5mm cancellous screws, positioned just laterally to the cartilage surface.











