
P. Beaufils, M. Thaunat, D. Passeron, P. Boisrenoult, N Pujol
326
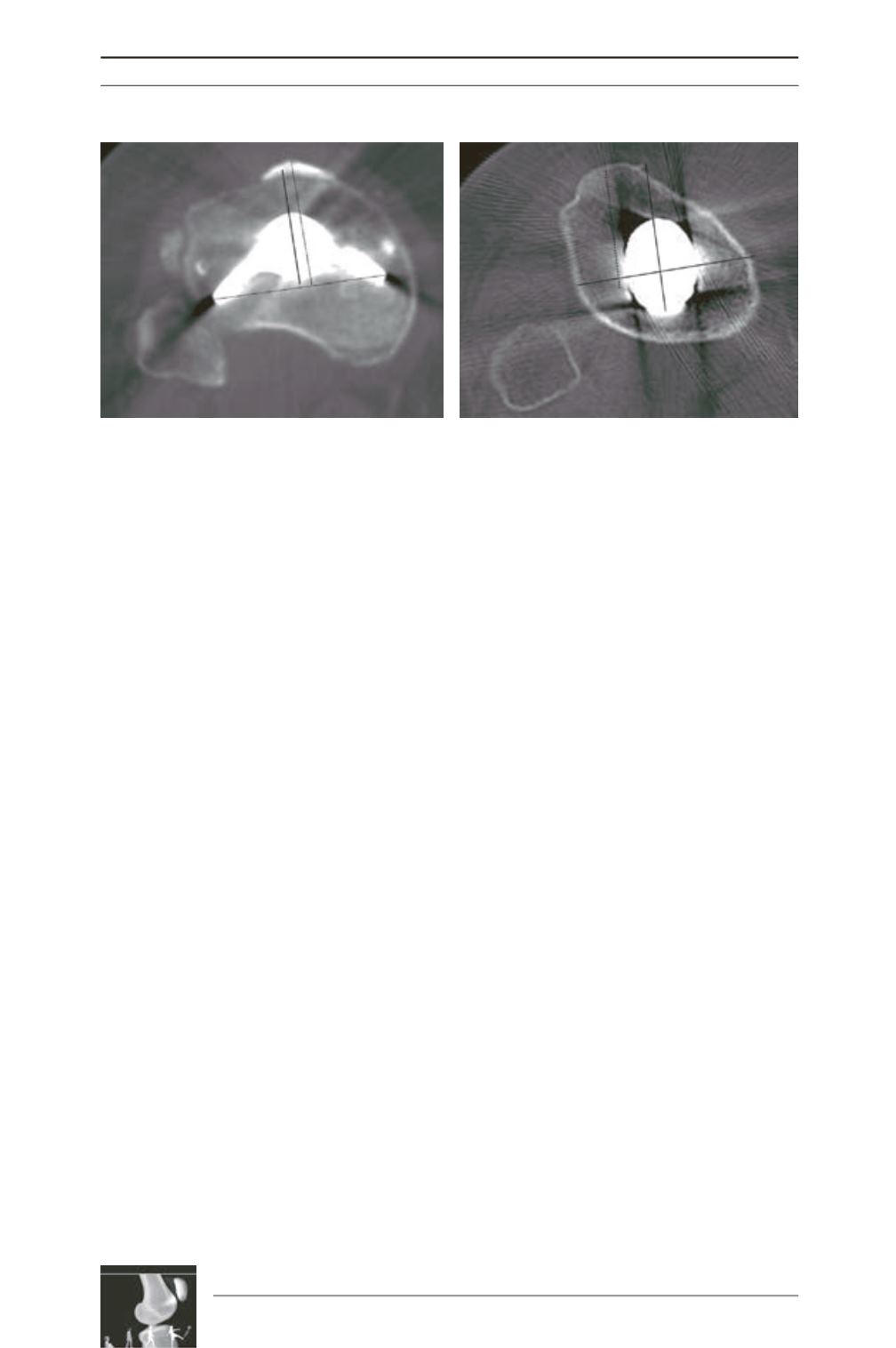
Fig. 5:
a) Example of external rotation by the lateral approach (The ATT is even medialized in relation to the center
of the keel).
b) And internal rotation by the medial approach.
a
b
Literature
[1] Abadie P, Galaud B, Michaut M, Fallet L,
Boisrenoult P, Beaufils P. Distal femur rotational
alignment and patellar subluxation: a CT scan in vivo
assessment.
Orthop Traum : Surg Res 2009 ;95: 267-71.
[2] Ammari T, Zniber B, Boisrenoult P,
Charrois O, Perreau M and Beaufils P. Patellar
position and lateral approach for total knee arthroplasty in
degenerative knees with lateral femoropatellar arthrosis.
Rev
Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 2005; 91: 215-21.
[3] Arnold MP, Friederich NF, Widmer H,
Muller W. Patellar substitution in total knee prosthesis,
important?
Orthopäde, 1998, 27, 637-41.
[4] Barrack RL, Bertot AJ, Wolfe MW. Patellar
resurfacing in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective
randomised double blind study with five to seven years of
follow-up.
J Bone Joint Surg (Am), 2001, 83, 1376-81.
[5] Beaufils P, Abouchaya A. Les reprises pour
l’appareil extenseur. In: Les reprises de prothèses totales de
genou. Symposium sous la direction de P. Burdin et D. Huten
(Réunion annuelle de la SOFCOT 2000).
Rev Chir Orthop,
2001, 87 (suppl au n° 5), 151-6.
[6] Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash
HE. Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after
total knee arthroplasty.
Clin Orthop Relat Res 1998; 356:
144-53.
[7] Berry DJ, Rand JA. Isolated patellar component
revision of total knee arthroplasty.
Clin Orthop, 1993, 286,
110-5.
[8] Bindelglass DF, Vince KG. Patellar tilt and
subluxation following subvastus and parapatellar approach
in total knee arthroplasty. Implication for surgical technique.
J Arthroplasty, 1996, 11, 507-11.
[9] Boyd AD, Ewald FC, Thomas WH, Poss R,
Sledge CB. Long term complications after total knee
arthroplasty with or without resurfacing of the patella.
J Bone Joint Surg (Am), 1993, 75, 761-81.
[10]
B
rick
GW, S
cott
RD. The patellofemoral component
of total knee arthroplasty.
Clin Orthop, 1988, 231, 163-78.
[11] Burki H, Von Knoch M, Heiss C, Drobny T,
Munzinger U. Lateral approach with osteotomy of the
tibial tubercle in primary total knee arthroplasty.
Clin
Orthop, 1999, 362, 156-61.
[12] Chan KC, Gill GS. Postoperative patellar tilt in total
knee arthroplasty.
J Arthroplast, 1999, 14, 300-4.
[13] Chang CH, Chen KH, Yang RS, Liu TK, Muscle
torques in total knee arthroplasty with subvastus and
parapatellar approaches.
Clin Orthop, 2002, 398, 189-95.
[14] CilaE, GuzelV, OzalayM, Ran J, Simsek SA,
Kanath U. Ozturk, Subvastus versus medial parapatellar
approach in total knee arthroplasty.
Arch Trauma Surg 265-
8002, 122.
[15] Doolittle KH, Turner RH. Patellofemoral
problems following total knee arthroplasty.
Orthop Rev,
1988, 17, 696-702.
[16] Engh GA, Holt BT, Parks NL. A midvastus
muscle-splitting approach for total knee arthroplasty.
J Arthroplasty 1997, 12 : 322.
[17] Faure BT, Benjamin JB, Lindsey B, Volz RG,
Schutte D. Comparison of the subvastus and paramédian
surgical approaches in bilateral knee arthroplasty.
J Arthroplasty 1993, 8, 511-6.
[18] Firestone TP, Teeny SM, Krackow KA. The
clinical and roentgenographic results of cementless porous-
coated patellar fixation.
Clin Orthop, 1991, 273, 184-9.











