S. Lustig, C. Scholes, S. Oussedik, M. Coolican, D. Parker
24
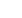
performance of the PSCB for tibial alignment
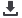
followed a similar pattern. The sagittal slope
displayed a larger range of values and a reduced
proportion of the sample within the 2°-3°
tolerance thresholds, compared to the coronal
alignment (Table 2). When the femoral and
tibial alignments were summed to produce a
virtual limb alignment, the PSCB would have
placed 79.3% of the sample within ±3° and
55.2% within ±2° of neutral (fig. 3). The total
sagittal alignment results were marked, with
54.5% and 32.7% within ±3° and ±2°,
respectively (Table 2).
The mean difference between planned coronal
alignment and intra-operative navigation
measurement collected preoperatively did not
differ significantly from zero (0.6±2.9, p=0.15)
although individual differences ranged from
−7° to 9.5°. The 99% prediction interval for a
single future measurement ranged from −7.2°
to 8.3°. The size of bone resection was similar
for the medial and lateral distal femoral cuts
(Table 3). The range for the difference between
the planned and the measured resections was
larger for the distal lateral cut, while the distal
medial cut displayed a wider prediction interval
(Table 3). The PSCB was within ±2mm of the
plan for 87.7% of the sample for both femoral
cuts. The mean differences between the plan
and the measured medial and lateral tibial
resections were not significantly different to
zero (Table 3).
Discussion
The hypothesis that the VISIONAIRE PSCB
system evaluated in this study is accurate was
not supported by the results. The PSCB resulted
in restoration to within 3° of the planned
coronal limb alignment in only 79.3% of cases
and of sagittal limb alignment in 54.5% of
cases as measured by intra-operative computer
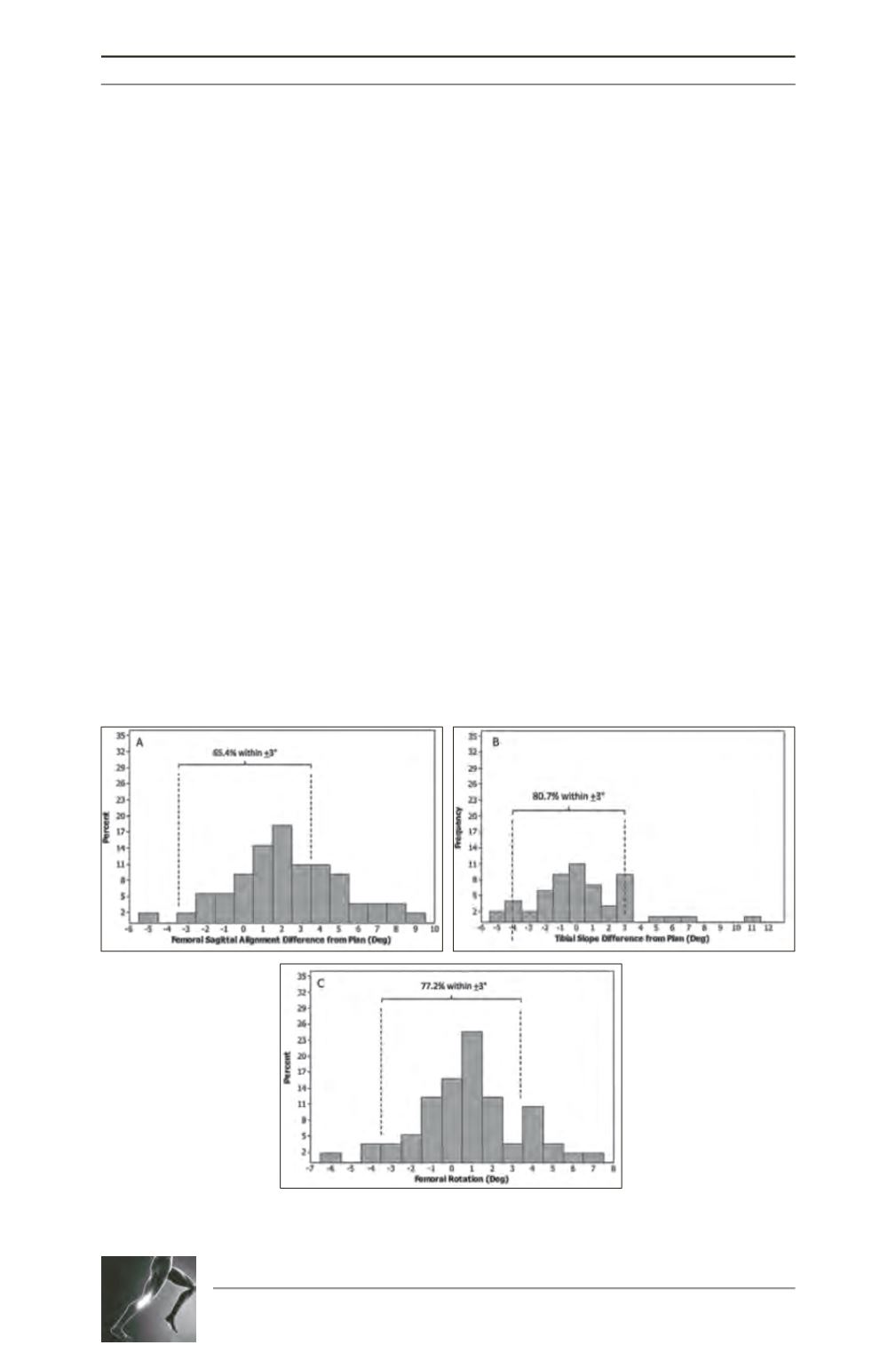
navigation. Femoral component rotation was
within 3° of the surgical trans-epicondylar axis
in 77.2% of cases. Whilst this compares
favourably with the accuracy of traditional jigs
[3, 4], it does not approach the accuracy
achieved with computer navigation [5, 6].
Fig. 3 : Sagittal alignment for the femoral (A) and tibial component (B)
and rotational alignment of the femoral component (C).