Accuracy of PSI: control with navigation
25
Potential sources of error in VISIONAIRE
cutting block design may include image
acquisition and interpretation of the 3D image
using MRIs about the knee joint limited to a
22cm field of view (11cm proximal and 11cm
distal to the joint line). This perhaps explains
the greater variation between the planned
sagittal alignment and the operative
measurements of the femoral and tibial
resections. The anterior bow of the femur
would tend to flex the apparent femoral sagittal
alignment measured from limited distal MR
slices (mean value ±2.1°), whilst the variation
in physiological posterior slope of the tibia [7]
would have an unpredictable effect on the
estimation of pre-operative tibial sagittal
alignment and therefore on the tibial resection
(mean value −0.1°, range −5° to +11°). Another
potential reason for inaccuracy could be the
error during the application of the PSCB on the
bone by the surgeon, even if the fitting was
reportedly good in every case for the 60 patients
in our study [8]. While the present results
quantify the error between the plan and the
blocks intraoperatively, the source of the error
remains to be identified. Nevertheless, the
results strongly suggest that the accuracy of the
system is inadequate for clinical use without
objective verification of alignment [9].
Conclusion
The VISIONAIRE PSCB system evaluated in
this study displayed unsatisfactory accuracy in
the coronal plane and even less accuracy in the
sagittal and rotational planes. While the present
study has quantified the error between the pre-
operative plan and the alignment derived from
the cutting blocks intraoperatively, the source
of error remains to be identified. We speculate
that limitations with the pre-operative imaging
protocol and its integration within the planning
process may provide opportunity for further
refinement. Nevertheless, despite the potential
of the system, the accuracy is inadequate for
clinical use without objective verification of
alignment. Further evaluation and protocol
refinement are necessary to avoid exposing
patients to the risk of poor outcomes due to
malalignment following total knee arthro
plasty.
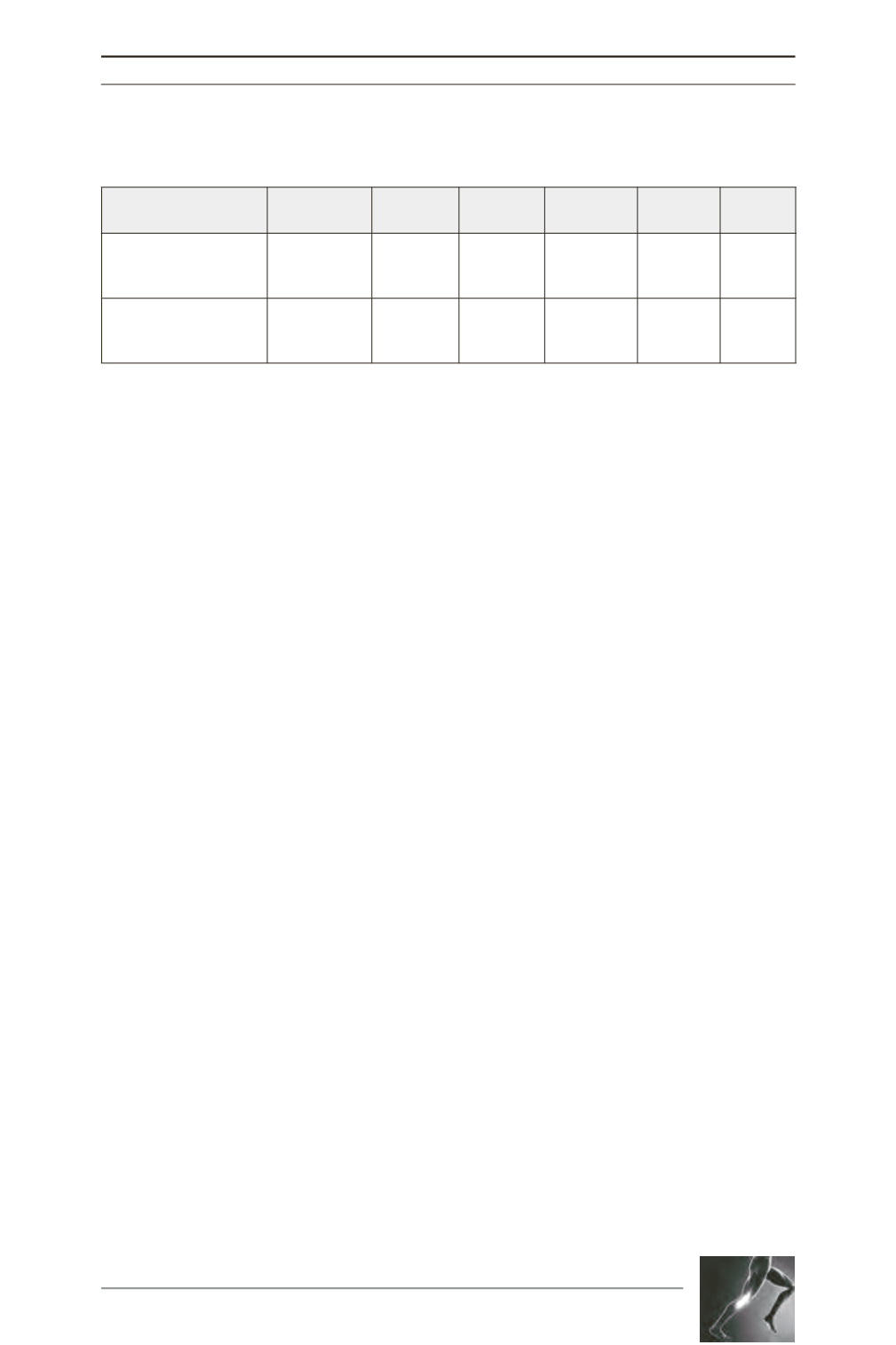
Table 3 : Differences between planned bone resections and bone resections
recorded from the VISIONAIRE PSCB intraoperatively (mm).
Difference P-value Range
% within
+2mm
% within
+1mm
99% PI
Femoral Resection
Distal Medial
Distal Lateral
0.0 + 1.2
0.25 + 1.1
1.0
0.1
-3.5, 6.5
-6.5, 6.5
87.7
87.7
70.2
66.7
-3.3, 3.3
-2.7, 3.1
Tibial Resection
Medial Plateau
Lateral Plateau
0.09 + 1.2
0.08 + 1.1
0.57
0.60
-6.0, 3.0
-7.0, 3.0
92
93
78.9
78.9
-3.0, 3.2
-3.0, 3.2