Robotic surgery and intelligent intruments - Patellofemoral Arthroplasties
51
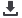
The kinematics of the virtually implanted
prosthesis can then be observed and the effect
of lateral release, MPFL reconstruction and
tibial tubercle osteotomy can also be evaluated
though computational methods. At present, this
step is time consuming and associated with
simplifications and estimations, and more
research is necessary to streamline the process
and validate model predictions. The proposed
benefit of the computational method is the
possibility of not only validating prosthesis
suitability based on geometrical criteria, but
also in terms of functional parameters such as
tracking and joint pressures (fig. 2).
Patient-specific
instrumentation
We prefer to have the most exact possible fit
between the prosthesis and the patient’s natural
femur distal, medial and lateral. The rotation of
the anterior cut in both the axial and sagittal
plane has an effect on the prosthesis articular
cartilage transition. The positive being that the
medial and lateral fit will influence the trochlear
groove alignment.
Once a satisfactory virtual implantation has
been achieved, which is usually a compromise
between a perfect prosthesis articular cartilage
transition, a satisfactory axial and rotational
alignment of the trochlear groove; a patient-
specific instrumentation can be designed
allowing for the precise positioning of the
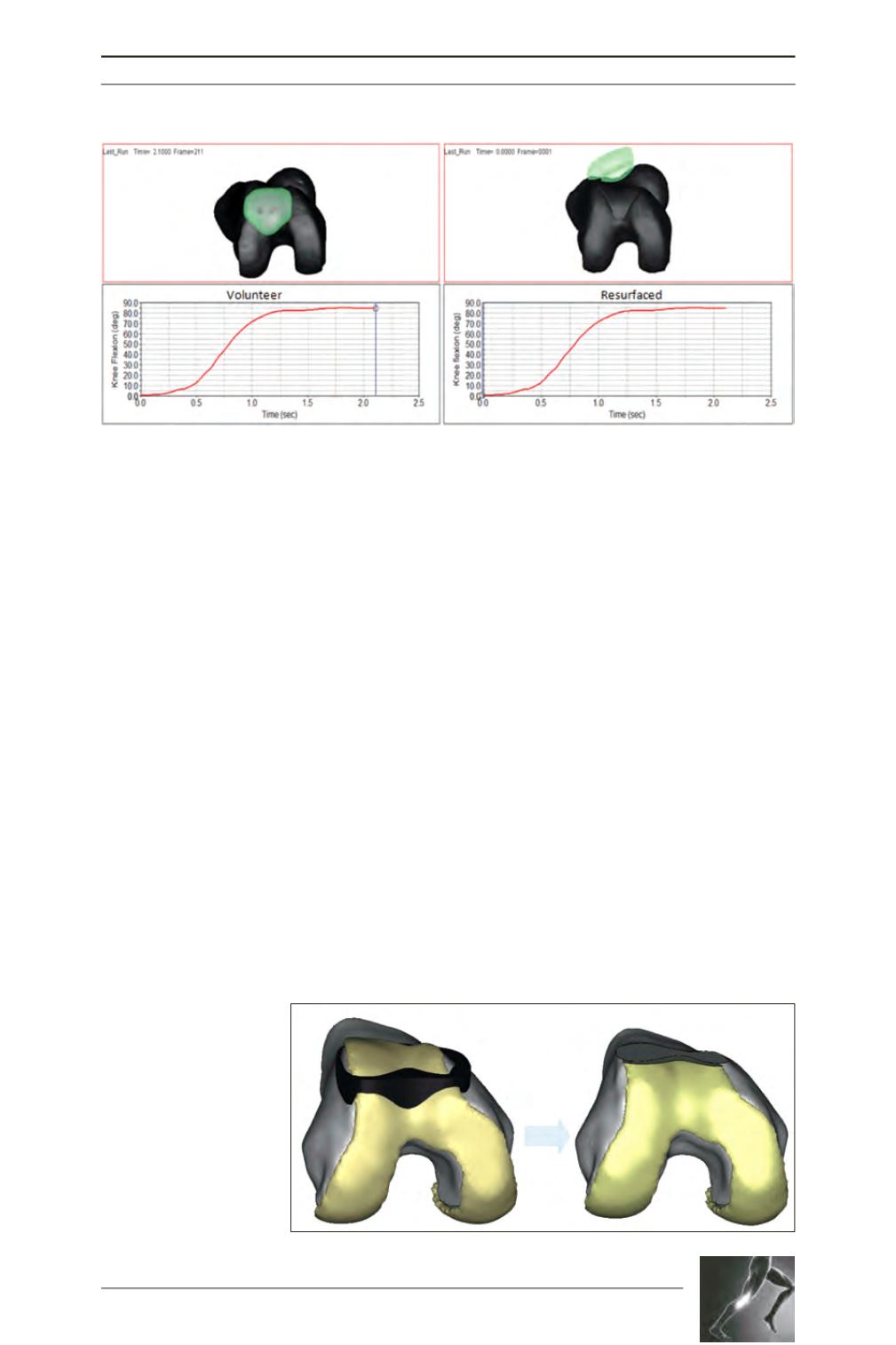
prosthesis. The patient-specific surgical tool
can reproduce the position of the anterior cut
made in the virtual space into the surgical
environment by conforming precisely to the
unique anatomy of the patient’s femur. The
anterior femoral cut is the only variable that we
can control (fig. 3).
Fig. 2: The tracking pattern of the volunteer’s knee and a resurfaced knee.
Fig. 3: The patient-specific
surgical tool conforms to
the patient’s anatomy to
reproduce the anterior cut
made in the virtual space.