P. Erasmus, K.J. Cho, J.H. Müller
52
Robotic bone
preparation
Two types of robots are available; haptic and
autonomous [2]. In haptic or tactile systems,
the surgeon drives the cutting tool but the robot
will prevent him to go off the pre-planned depth
and position of the bone cuts. In the autonomous
systems, the surgeon will do the approach, set
up the robot and then stand back allowing the
robot to do the bone cuts by itself.
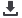
With the haptic systems, a preoperative
planning is done on 3D reconstructions from
the CT and MRI. At the surgery, a surgeon
would use the computer to determine the leg
alignment and “morph” the joint surfaces in the
same way as the CAD surgery. In contrast to
CAD surgery, the bone cuts are now made
under robotic control according to the
preoperative planning (fig. 4).
However, even in these robotic systems a best
fit is usually a compromise between a good
prosthesis articular transition; and an acceptable
axial and sagittal rotation of the prosthesis.
Patient-specific
prosthesis
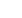
In a study where we virtually implanted 4
different commercially available prosthesis in a
normal asymptomatic patellofemoral joint, it
was evident that not one of these prosthesis
restored the joint to normal [3]. All four
prosthesis;
the
Avon
TM
Patellofemoral
Arthroplasty (Stryker, Kalamazoo, Michigan,
USA); the Competitor PFJ Oxinium (Smith &
Nephew, Inc. Memphis, Tennessee, USA); the
Vanguard
TM
PatellofemoralReplacement System
(Biomet UK L
td
, South Wales, UK); and the
Kneetec, (Tornier, Fr) increased the medial A-P
dimension, decreased the lateral A-P dimension
and decreased the depth of the trochlea (fig. 5).
Fig. 4: Morphing the distal femur and planning the prosthesis position with the aid of a computer for
implanting the prosthesis using a haptic robot (Navio PFSTM surgical system, Blue belt technologies, INC).
Fig. 5: Virtual implantation of 4 different commercial off the shelve prostheses implantation shows raised
medial A-P dimensions relative to lateral A-P dimensions and decreased trochlear depth.